• Huaxiao Stainless steel suppliers •
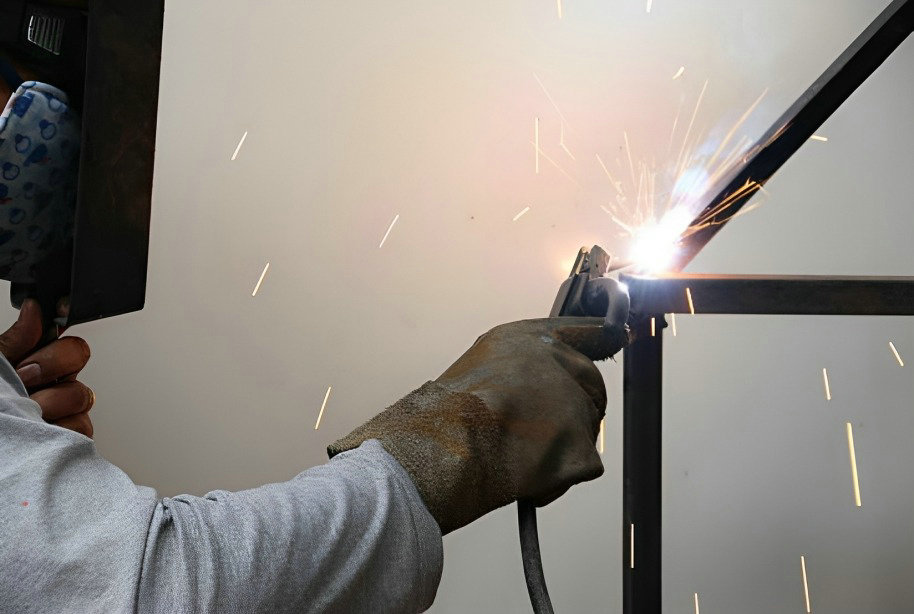
how to TIG weld stainless steel?
Stainless steel, renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, finds wide application across various fields. Among the numerous methods for connecting stainless steel, TIG welding stands out for its high-quality welds and extensive application range. So, how can one proficiently master TIG welding techniques to ensure the quality and effectiveness of stainless steel welding? This article will reveal the key steps and precautions for TIG weld stainless steel, aiding you in effortlessly mastering this practical skill.

-Huaxiao stainless steel suppliers
Preparation——TIG weld stainless steel
- Before welding, it is essential to inspect the areas of the workpiece to be welded for any oxides, grease, coatings, or other debris. Strict cleaning is necessary prior to welding to prevent poor fusion formation or even inadequate penetration, which may compromise the quality.
- Prior to welding, familiarize yourself with the technical requirements of the drawings and strictly follow the construction according to the drawing requirements. After positioning the welding parts according to the dimensions of the drawing, use process braces or reinforcements to prevent or minimize welding deformation during the welding process, ensuring product quality.
- Before welding, check if the tungsten electrode used matches the current welding plate thickness. Otherwise, replace it with a suitable tungsten electrode.
- Before performing TIG weld stainless steel, the length of the tungsten electrode extending from the nozzle is generally taken as 1 to 2 times the diameter of the tungsten electrode.
- Before welding, open the valve of the argon gas cylinder, select the appropriate welding flow rate of argon gas, current, and stainless steel welding wire. Specific values are provided in the table below.
| Plate thickness | Welding wire diameter | Tungsten electrode diameter | Tungsten electrode taper | Welding current | Maximum gas flow rate |
| 0.4 | 1.0 | 1.0-1.6 | 12 | 5-20 | 2.5 |
| 0.6 | 1.0 | 1.0-1.6 | 20 | 15-30 | 2.5 |
| 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.0-1.6 | 25 | 25-50 | 3 |
| 1.5 | 1.2 | 1.0-1.6 | 30 | 50-75 | 4 |
| 2.5 | 1.5 | 1.6-2.4 | 35 | 65-96 | 6 |
| 3.0 | 1.5 | 1.6-2.4 | 45 | 90-120 | 7 |
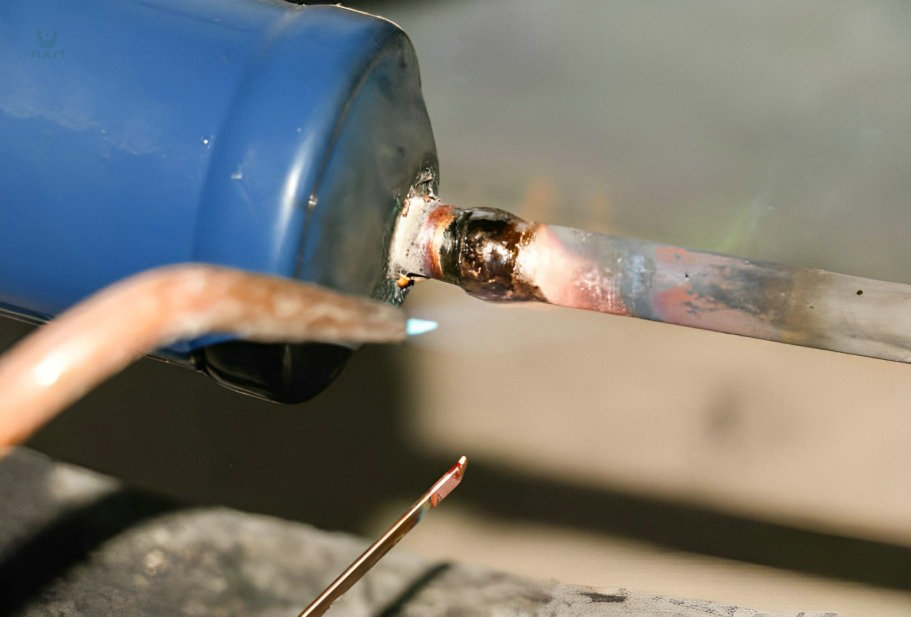

-Huaxiao stainless steel suppliers
What's Challenging About Welding Stainless Steel
1. Thermal Expansion and Warping
Stainless steel has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion compared to carbon steel. This means it expands and contracts more when exposed to heat. During welding, this can lead to significant warping and distortion if not properly managed.
Solutions:
- Use fixtures and clamps to hold the workpieces in place.
- Employ intermittent welding techniques to minimize heat input.
- Allow the material to cool down between passes.
2. Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ) Sensitivity
The heat-affected zone (HAZ) in stainless steel is particularly susceptible to sensitization and corrosion. This can occur when the material is heated to high temperatures, causing the chromium to combine with carbon and form chromium carbides. This reduces the amount of chromium available to form the protective oxide layer, leading to intergranular corrosion.
Solutions:
- Use low-carbon grades of stainless steel (e.g., 304L, 316L) to reduce carbide formation.
- Apply post-weld heat treatments to restore the chromium distribution.
3. Oxidation and Discoloration
Stainless steel can oxidize and discolor when exposed to high temperatures during welding. This oxidation can compromise the material’s corrosion resistance and aesthetics.
Solutions:
- Shield the weld area with an inert gas, such as argon or helium, to prevent oxidation.
- Use a back-purge gas to protect the underside of the weld.
- Clean the weld area thoroughly before and after welding to remove any oxide layers.
4. Maintaining Corrosion Resistance
Maintaining the corrosion resistance of stainless steel is a critical concern during welding. Improper techniques can introduce contaminants or cause changes in the microstructure that reduce the material’s ability to resist corrosion.
Solutions:
- Use filler materials that match or exceed the corrosion resistance of the base material.
- Avoid cross-contamination with carbon steel tools and equipment.
- Perform passivation treatments after welding to restore the protective oxide layer.
5. Weldability of Different Grades
Not all grades of stainless steel have the same weldability. Austenitic stainless steels, such as 304 and 316, are generally easier to weld, while martensitic and ferritic stainless steels can be more challenging.
Solutions:
- Choose the appropriate welding method and parameters based on the specific grade.
- Preheat and post-heat treatments may be necessary for certain grades to avoid cracking.
6. Cracking Issues
Stainless steel is prone to various forms of cracking, such as hot cracking and stress corrosion cracking. These issues can arise due to improper welding techniques or unfavorable metallurgical conditions.
Solutions:
- Control the cooling rate to avoid thermal stresses.
- Use welding techniques that minimize residual stresses, such as controlled heat input and proper joint design.
- Regularly inspect welds for signs of cracking and address any issues promptly.
-Huaxiao stainless steel suppliers
Techniques For TIG Welding Stainless Steel
Select Proper Tungsten Electrode
- Use a 2% thoriated (red), 2% lanthanated (blue), or ceriated (orange) tungsten electrode for stainless steel TIG welding. Thoriated electrodes are common for their durability and stable arc characteristics.
- The tungsten tip should be sharpened to a point to achieve a stable arc and better control.
Set Correct Shielding Gas Flow
- TIG welding requires an inert shielding gas, typically 100% argon for stainless steel. The gas protects the weld pool from oxygen and other atmospheric gases that can cause oxidation or contamination.
- The typical flow rate for argon is between 15 to 20 cubic feet per hour (CFH), but this can be adjusted based on the welding conditions.
Use a Backing Gas or Purge
- To prevent oxidation or discoloration on the backside of the weld (commonly known as “sugaring”), use a back purge with argon gas on the reverse side of the stainless steel joint.
- This is particularly important for butt joints or thin stainless steel. Purging ensures the entire weld is shielded from oxygen and results in a cleaner, stronger weld.
Control Heat Input
- Stainless steel is highly sensitive to heat, and too much heat can lead to warping, distortion, or discoloration of the metal. Use a low amperage setting and move the torch at a steady pace to minimize heat input.
- Utilize a pulsing technique to control heat. Pulsing allows better control over the weld pool and reduces the overall heat exposure, minimizing the chances of distortion.
The Process of TIG Weld Stainless Steel
- Adjust electrode and wire distance: The extension length of the tungsten electrode from the nozzle is generally set to 1-2 times the diameter of the tungsten electrode, and the distance from the workpiece (arc length) should generally not exceed 1.5 times the diameter of the tungsten electrode.
- Control welding speed and angle: Maintain a stable welding speed, approximately 250-300 millimeters per minute; the angle between the welding wire and the workpiece is 10 degrees, and the angle between the tungsten electrode welding gun and the workpiece is 75 degrees.
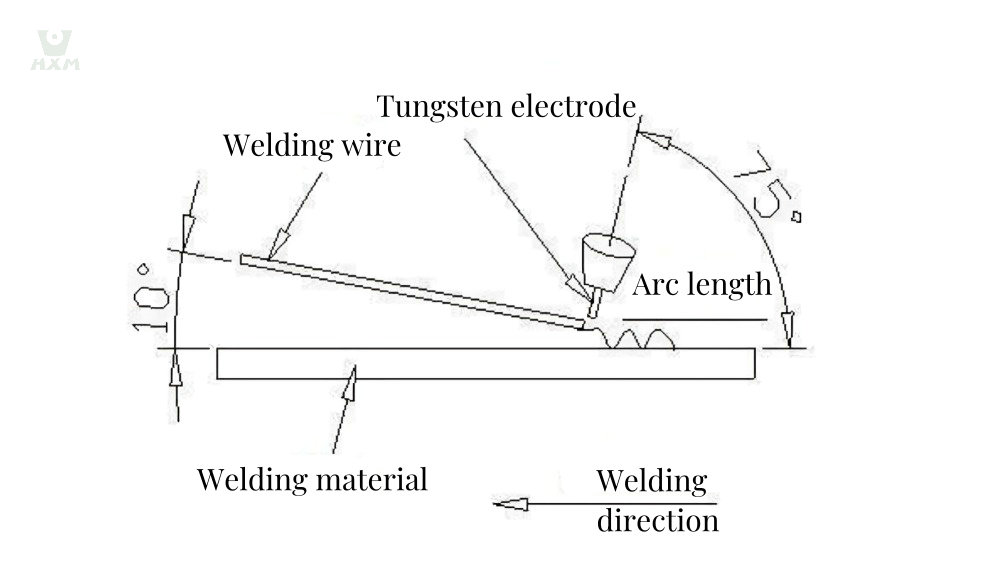
- Stable posture and wire feeding: During the welding process, maintain a stable posture, and the welding wire should be fed into the molten pool at a constant speed.
- Monitor weld quality: Ensure uniform width of the weld seam, consistent height, and a visually appealing appearance.
- Pay attention to environmental factors: Avoid using fans during welding to prevent the protective gas from being dispersed; ensure the fan inside the welding machine operates normally.
- Continuously monitor welding quality: Continuously monitor welding quality during the welding process to avoid defects such as weld beads or incomplete penetration.

-Huaxiao stainless steel suppliers
Post TIG weld stainless steel procedures
- Remove welding jigs: After the welded parts have cooled down, remove the welding jigs.
- Treat welding scars: Grind down welding scars to ensure a smooth surface.
- Clean spatter: Remove welding spatter and other debris to maintain cleanliness of the welded product.
- Post-weld correction: Perform necessary post-weld corrections according to blueprint requirements to ensure product quality.
- Documentation: Conduct self-inspection of products according to blueprints and process requirements, and meticulously fill out relevant documents such as daily production reports and operation cards.
conclusion
In this blog, we delve into the key steps and considerations of TIG weld stainless steel. From meticulous preparation before welding, to precise execution during operation, and meticulous handling afterward, each step reflects respect for the process and pursuit of quality. TIG weld stainless steel, as a high-quality welding method, is undeniably important in the manufacturing of stainless steel products.
TIG weld stainless steel is not just a technique, but also a commitment to quality. At Huaxiao Metal, we have been in the stainless steel export industry for many years, always dedicated to providing customers with high-quality stainless steel products. If you have any needs, please feel free to contact us, and we will be happy to serve you.









