Is Stainless Steel Waterproof?
Is stainless steel waterproof? From gleaming kitchen appliances to sturdy bridges spanning waterways, stainless steel plays a vital role in a plethora of applications that often involve exposure to water. But when we pose the intriguing question, “Is Stainless Steel Waterproof?” we embark on a journey through the fascinating world of this remarkable alloy and its interactions with moisture. Whether you’re contemplating stainless steel for maritime ventures, kitchen renovations, or any water-related project, this article will quench your curiosity and leave you with a deeper understanding of this versatile material’s relationship with H2O. Let’s set sail into the realm of stainless steel’s waterproof mysteries.
Is stainless steel waterproof?
Yes, stainless steel is not only resistant to water but also largely impervious to its effects. Its inherent corrosion resistance, achieved through the formation of a passive chromium oxide layer on the surface, makes it highly waterproof. This layer acts as a shield, preventing water from penetrating the material and causing rust or degradation. Stainless steel’s ability to repel water is due to its low surface energy, which causes water droplets to form into beads that easily roll off.
In practical applications, stainless steel is widely used in environments with constant exposure to water, such as marine equipment, kitchen appliances, and architectural structures. Its durability and resistance to corrosion make it an ideal choice for situations where other metals might succumb to water-induced damage.
So, in essence, stainless steel can be considered waterproof, thanks to its innate ability to withstand the corrosive effects of water and moisture, making it a trusted choice in a wide range of water-related scenarios.
Practical Applications of Stainless Steel in
Water-Related Environments
In the realm of water-related applications, stainless steel plays an integral role across various industries, owing to its remarkable waterproof properties. Stainless steel’s innate resistance to water-related challenges makes it indispensable in several sectors, including:

Marine Industry
Stainless steel is a cornerstone of the marine industry, where exposure to saltwater and the harsh marine environment demands materials with exceptional corrosion resistance. It is employed in shipbuilding, from hulls to railings, offering longevity and protection against water-induced deterioration. Stainless steel supplier cater to the specific needs of this industry by providing corrosion-resistant grades.
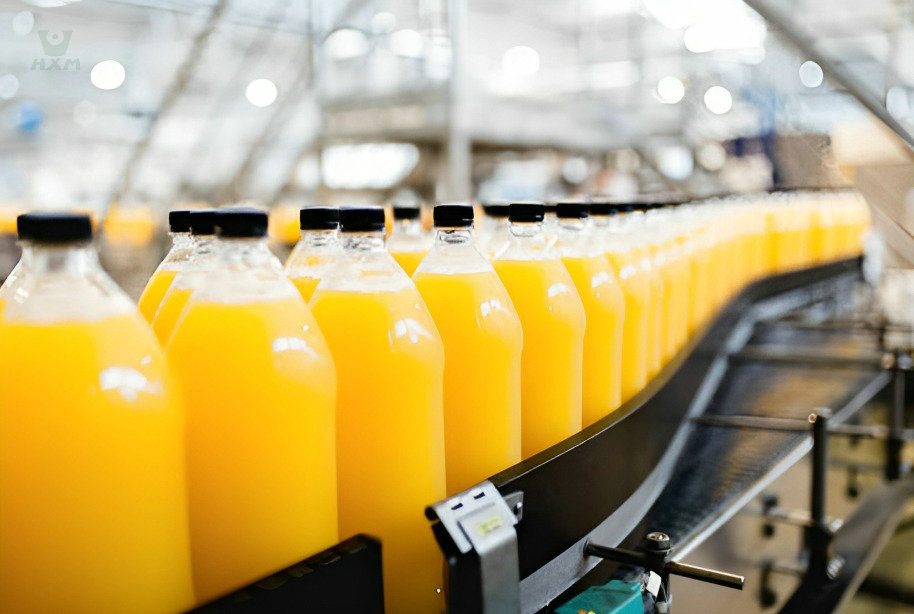

Food and Beverage
Stainless steel is ubiquitous in food and beverage processing. Its waterproof nature ensures a hygienic environment where water, steam, and sanitation are constants. Whether it's stainless steel tanks for beverage storage or food-grade equipment for processing, stainless steel maintains its integrity even in prolonged contact with water.
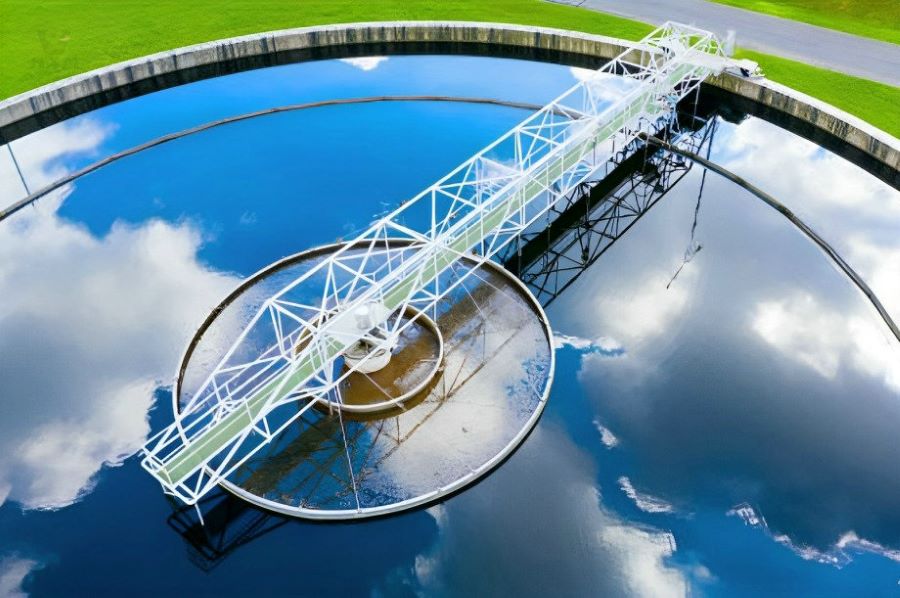

Water Treatment
In the vital field of water treatment, stainless steel is used in pipes, valves, and equipment due to its resistance to corrosion by treated water and chemicals. Its waterproof characteristics enable the construction of durable and long-lasting infrastructure, ensuring the safety and quality of drinking water.

Architecture and Construction
Stainless steel's application extends to architectural elements exposed to the elements, like bridges, roofing, and facades. Its ability to resist corrosion from rain and moisture is vital for maintaining structural integrity and aesthetics.
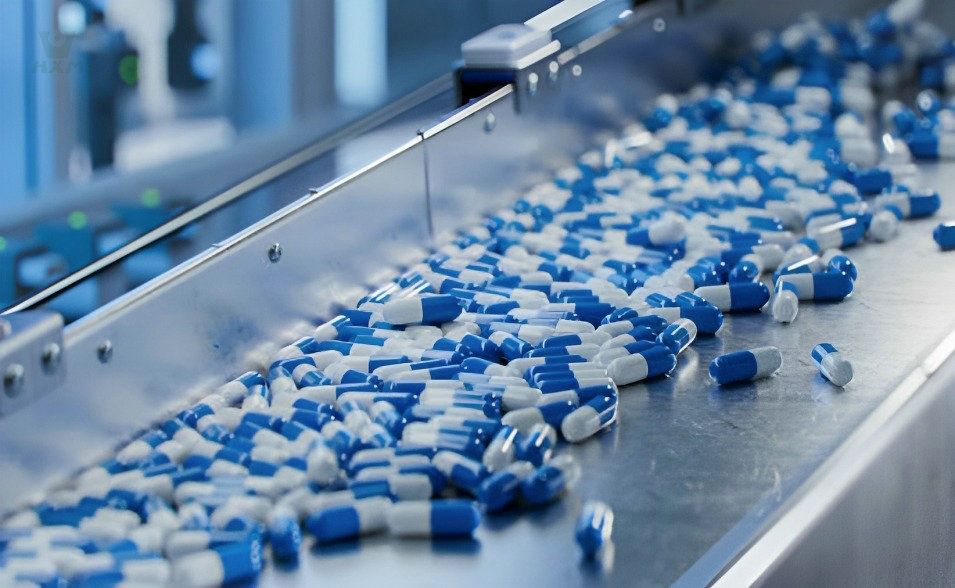

Medical and Pharmaceutical
In medical and pharmaceutical settings, where stringent cleanliness and sanitation are imperative, stainless steel's waterproof properties are invaluable. From wash basins to laboratory equipment, stainless steel helps maintain a sterile environment resistant to water and cleaning agents.

Agriculture
The agricultural sector benefits from stainless steel in various ways, particularly in irrigation systems, tanks, and machinery components exposed to water, soil, and fertilizers. Its waterproof nature safeguards against corrosion in these demanding conditions.
These examples illustrate how stainless steel’s inherent waterproof qualities are leveraged to ensure durability and performance in diverse water-related applications. Stainless steel supplier offer a range of grades optimized for each industry’s specific requirements, guaranteeing that stainless steel remains a cornerstone of waterproof engineering.
The Science Behind
Stainless Steel's Waterproof Properties
Stainless steel’s exceptional waterproof properties are intricately linked to its composition and microstructure. Understanding the science behind it is crucial to grasp its waterproof nature.
composition and structure of stainless steel
- Composition: Stainless steel is primarily composed of iron, with chromium as the essential alloying element. Chromium content typically ranges from 10% to 30%. This chromium content forms a passive oxide layer on the steel's surface when exposed to oxygen, which renders it highly resistant to corrosion. In addition to chromium, nickel and molybdenum are often added to enhance corrosion resistance, which is vital for its waterproof quality.
- Microstructure: Stainless steel's microstructure is predominantly austenitic, ferritic, or martensitic, depending on the specific grade and composition. Austenitic stainless steel, characterized by a face-centered cubic (FCC) crystal structure, is renowned for its superior corrosion resistance and waterproof nature. This microstructure facilitates the formation of a protective oxide layer when in contact with water or oxygen, preventing the underlying material from rusting or corroding.
- Alloying Elements: The addition of other elements like nickel, molybdenum, and nitrogen significantly influences stainless steel's waterproof capabilities. For instance, nickel enhances the stability of the passive oxide layer, further protecting the material from water-induced corrosion.
- Stainless Steel Supplier: Stainless steel supplier play a pivotal role in tailoring stainless steel to meet specific waterproof requirements. They provide various grades optimized for different applications, ensuring the right alloy is chosen to combat corrosion in various water-related environments.
- Corrosion Resistance: The key to stainless steel waterproof quality lies in its remarkable corrosion resistance. The passive oxide layer formed on its surface when exposed to moisture prevents water from penetrating the material and causing structural damage. This corrosion-resistant shield remains intact even in prolonged contact with water.
In summary, stainless steel waterproof nature is a result of its unique composition, microstructure, and the addition of alloying elements like chromium, nickel, and molybdenum. This combination forms a robust, corrosion-resistant material that can effectively withstand exposure to water, making it indispensable in a wide range of applications, from marine environments to food processing and water treatment facilities.
the formation of the chromium oxide layer
The formation of the chromium oxide layer is a fundamental process that contributes to stainless steel waterproof properties. Understanding this mechanism sheds light on how stainless steel remains impervious to water-induced corrosion.
- Initial Exposure to Oxygen: When stainless steel is exposed to oxygen, either from the atmosphere or water, the surface begins to react. In the presence of moisture, a thin layer of water molecules adheres to the steel's surface.
- Chromium Content: Stainless steel's composition plays a critical role. Chromium content, typically at least 10%, is a key factor. Chromium has a natural affinity for oxygen, and it readily reacts with oxygen molecules from the air or water.
- Oxidation Process: The chromium atoms on the steel's surface react with the oxygen to form chromium oxide (Cr2O3). This reaction is highly exothermic, meaning it releases heat. The heat generated helps to accelerate the formation of the oxide layer.
- Passivation: The chromium oxide layer formed on the surface of stainless steel is a passive, or inert, layer. It is this passive layer that makes stainless steel waterproof. The passive oxide layer is stable and does not react further with the surrounding environment. As a result, it acts as a protective barrier, preventing the underlying metal from coming into contact with water or other corrosive substances.
- Self-Healing Property: An intriguing characteristic of stainless steel is its ability to self-heal the chromium oxide layer if damaged. Even if the passive layer is scratched or compromised, the exposed metal immediately reacts with oxygen in the air or water to form a new protective oxide layer. This self-healing property ensures the continued stainless steel waterproof nature.
In conclusion, stainless steel waterproof qualities stem from the remarkable formation and presence of the chromium oxide layer. This thin, stable, and self-renewing layer acts as a protective barrier, preventing water from reaching the underlying metal and causing corrosion. It is this inherent property that makes stainless steel indispensable in various applications where exposure to moisture and water is a constant challenge.
How this layer makes stainless steel resistant to water?
The presence of the chromium oxide layer on stainless steel is instrumental in making it highly resistant to water. This layer’s characteristics and interactions with water contribute to stainless steel waterproof nature:
- Inert and Stable Barrier: The chromium oxide layer is inert, meaning it does not readily react with the surrounding environment, including water. This stability prevents the layer from breaking down in the presence of moisture.
- Preventing Corrosion: The primary purpose of this oxide layer is to act as a shield that prevents water from reaching the underlying metal. Water can contain corrosive elements, such as oxygen and chloride ions, which can cause corrosion in metals. However, the waterproof chromium oxide layer serves as a barrier, ensuring water molecules do not directly interact with the metal's surface.
- Self-Healing Property: Even if the chromium oxide layer is damaged or scratched, it possesses a remarkable self-healing property. When the layer is compromised, the exposed metal immediately reacts with oxygen from the air or water to form a new oxide layer. This rapid reformation ensures the continued integrity of the waterproof barrier.
- Maintaining Aesthetic Appearance: The stainless steel waterproof nature helps maintain its aesthetic appearance over time. Water, with its potential to cause rust and corrosion in other materials, does not have the same effect on stainless steel. This ensures stainless steel retains its shine and durability even in wet environments.
In summary, the stainless steel waterproof nature is a result of the chromium oxide layer that forms on its surface. This layer acts as a stable, inert barrier, preventing water from causing corrosion or degradation of the metal. Its self-healing property ensures long-term protection against water-induced damage, making stainless steel a versatile and durable choice in countless applications.
How to test stainless steel waterproof?
When it comes to determining the waterproof capabilities of stainless steel, specific tests and certifications are available to evaluate its performance in resisting water ingress. These tests help assess the suitability of stainless steel for different applications where water resistance is critical.
immersion test
The immersion test is a common method used when evaluating stainless steel waterproof performance. This test simulates water contact under actual conditions of use by completely immersing a stainless steel sample in water for a certain period of time. The purpose of this test is to evaluate the corrosion resistance and water resistance of stainless steel when exposed to water for extended periods of time.
The immersion test typically involves placing the stainless steel sample in water, either tap water or a solution under specific water quality conditions. The duration of the test can be a few hours, a few days or longer depending on the application requirements. During the immersion process, the sample should be completely covered with water to ensure adequate contact with the water.

-Huaxiao Stainless Steel Supplier
After testing is complete, the stainless steel sample is removed for observation and evaluation. The focus of the inspection is to look for any possible signs of corrosion, such as rust spots, discoloration, stains, pits, etc. These signs may indicate that the water resistance of the stainless steel has been compromised, especially if there are visible signs of corrosion.
The immersion test can provide preliminary information about the water resistance of stainless steel in the case of water use. However, it is important to note that the water quality, temperature, water pressure and other environmental factors in the actual application may have an effect on the water resistance of stainless steel. Therefore, the actual conditions of use as well as other factors need to be taken into account when performing the results of the immersion test.
Salt spray test
Salt spray testing is a common method used when evaluating the stainless steel waterproof performance. This test is designed to simulate environmental conditions with high salinity and corrosiveness to evaluate the corrosion resistance and water resistance of stainless steel under such conditions.
Salt spray testing typically uses brine spray equipment to produce a water spray containing salt. The stainless steel sample is placed in a test chamber and the brine solution is then sprayed in a mist onto the sample surface by the spray equipment. Test conditions can be adjusted as required, including spray time, spray interval, and test period.
During the salt spray test, the stainless steel sample is exposed to the brine spray to simulate the corrosive conditions in a real environment. The length of the test time can vary depending on the actual requirements and can usually be a few hours, a few days, or even longer.
At the end of the test, the stainless steel sample is removed and evaluated. Observations are focused on looking for any possible signs of corrosion, such as rust spots, corrosion patches, pits, etc. These signs can indicate the water resistance and corrosion resistance of the stainless steel, especially if there are visible signs of corrosion.
The results of salt spray testing can provide information on the water resistance of stainless steel in high salinity and corrosive environments. However, it is important to note that actual use conditions and environments may vary, so test results are for reference only. Other factors, such as the composition of the material, surface treatment, use environment, and maintenance measures, can also affect the stainless steel waterproof performance.
-Huaxiao Stainless Steel Supplier
Stainless Steel as Waterproof Misconceptions & Challenges
Key points would include:
Misconception of Waterproofing: Explaining that while stainless steel is corrosion-resistant, prolonged exposure to water, especially seawater or chlorinated water, can lead to pitting or corrosion in certain grades.
Types of Stainless Steel and Water Resistance: Discussing which stainless steel grades, such as 304 or 316, are more resistant to water-related damage and under what conditions they perform best.
Challenges in Harsh Environments: Highlighting the environmental factors that can challenge stainless steel’s resistance, including salinity, chlorine, and acidic conditions.
Maintenance for Long-Term Durability: Providing tips on how to maintain stainless steel in wet or humid conditions to ensure its longevity.
How to protect stainless steel?
To ensure long-term stainless steel waterproof properties, it is important to follow recommended maintenance practices. While stainless steel is inherently resistant to corrosion and water damage, proper care and maintenance can further enhance its performance. Here are some recommended practices:
- Regular Cleaning: Regularly clean the stainless steel surfaces using mild soap or detergent and warm water. Gently scrub with a soft cloth or sponge to remove dirt, grime, and water spots. Avoid using abrasive cleaners or scrubbing pads that can scratch the surface.
- Thorough Drying: After cleaning, thoroughly dry the stainless steel surfaces with a clean, lint-free cloth. Moisture left on the surface can lead to water spots or staining over time, so ensure the surface is completely dry.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Avoid using harsh chemicals or cleaners containing chlorine or bleach on stainless steel, as they can damage the protective oxide layer and compromise its waterproof properties.
- Remove Salt Deposits: If the stainless steel is exposed to salt water or coastal environments, it is crucial to remove any salt deposits regularly. Rinse the surface with fresh water to remove salt residue and then dry it thoroughly to prevent corrosion.
- Maintain Passivation: Passivation is a process that enhances the corrosion resistance of stainless steel. If the stainless steel surface loses its shine or develops signs of rust, consult with a stainless steel supplier or professional to assess if passivation is required. They can guide you on the appropriate procedures and products to restore the protective oxide layer.
- Protect Against Physical Damage: Avoid scratching or damaging the stainless steel surface, as it can compromise its water resistance. Use protective pads or mats under heavy objects and avoid dragging or sliding items across the surface.
- Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect the stainless steel surfaces for any signs of damage, corrosion, or water ingress. Promptly address any issues to prevent further deterioration and ensure the long-term water resistance of the stainless steel.
By following these recommended maintenance practices, you can help maintain the water resistance of stainless steel over the long term. Consulting with a reputable stainless steel supplier can provide valuable insights and guidance on specific maintenance requirements based on the grade and finish of the stainless steel you are using.
conclusion
In conclusion, stainless steel is known for its remarkable water resistance, thanks to its composition and the protective chromium oxide layer on its surface. With its inherent corrosion resistance, stainless steel is well-suited for various applications that involve exposure to water or moisture.
By implementing proper maintenance practices, you can ensure the long-term water resistance of stainless steel. Regular cleaning, thorough drying, and avoiding harsh chemicals are essential steps in preserving its protective properties. Additionally, removing salt deposits, maintaining passivation, and protecting against physical damage are crucial for sustaining its water resistance.
Remember to periodically inspect the stainless steel surfaces and promptly address any issues to prevent further damage. Consulting with a reliable stainless steel supplier can provide valuable guidance and support tailored to your specific needs.
Whether it’s architectural structures, marine equipment, or kitchen appliances, stainless steel’s water resistance makes it a reliable and durable choice. With proper care and maintenance, stainless steel can continue to showcase its exceptional water-resistant properties and maintain its aesthetic appeal for years to come.