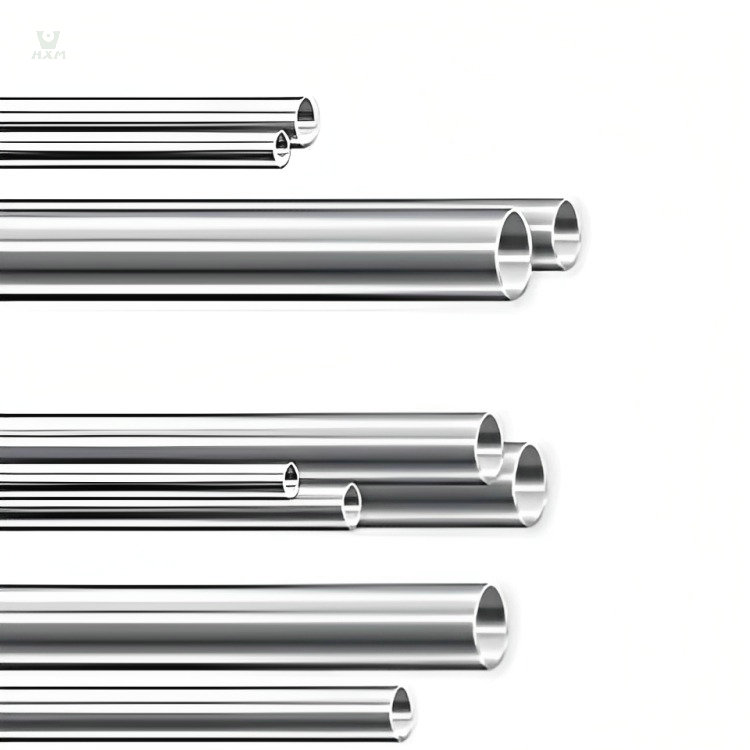
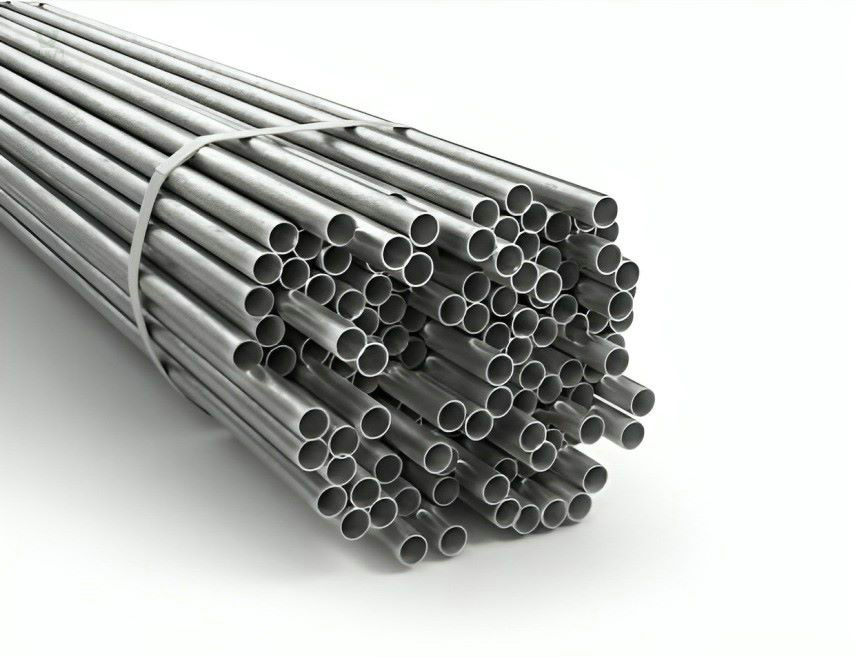
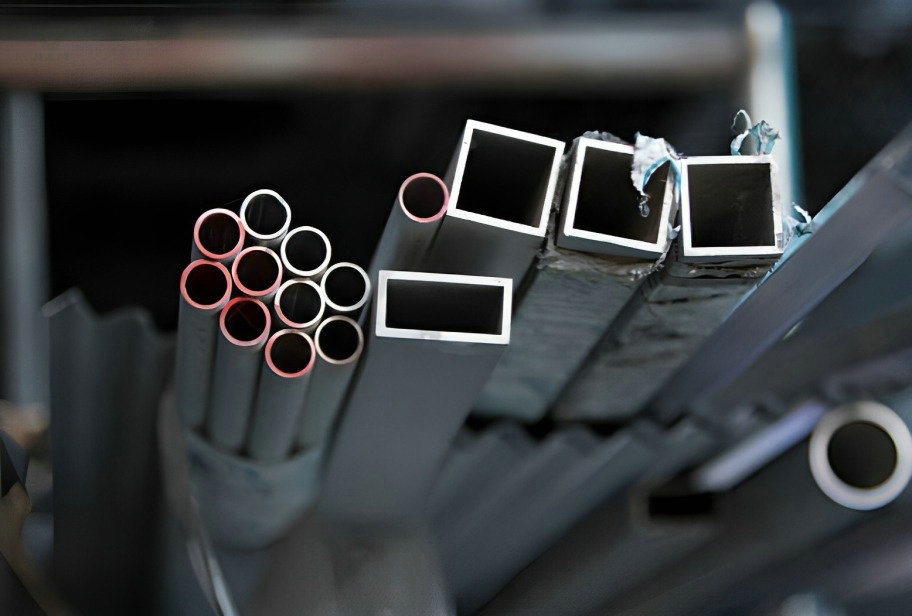
Stainless Steel Condenser Tube Supplier
ASME SB-167 ASME SB-423 ASME SB-163 ASME Sb338
ASME SA789 Seamless and Welded Ferrite/Austenitic Stainless Steel Tube for General Use
ASME SA213 Seamless Ferrite and Austenitic Alloy Steel Tube for Boiler, Superheater and Heat Exchanger
ASME SA249 Welded Austenitic Steel Tube for Boiler, Superheater, Heat Exchanger and Condenser Tube
Product Description of Stainless Steel Condenser Tube
Stainless steel condenser tubes are a type of tubing used in condensation applications and are usually made of stainless steel material. They are widely used in various industries for cooling and condensing processes in order to convert vapors or gases into a liquid state. The design and material selection of these condenser tubes enable them to operate effectively in harsh environments while providing excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity.
The size of the heat exchanger tube plays a crucial role in heat transfer efficiency, as it directly influences the heat exchange surface area within the heat exchanger. When the heat exchanger tubing has a smaller diameter, it results in a larger heat exchange area per unit volume, contributing to a more compact and space-efficient design. Moreover, utilizing smaller diameter tubes reduces the alloy consumption required for each unit of heat exchange area, contributing to cost savings. Additionally, the use of smaller diameter tubes tends to enhance the heat transfer coefficient, thereby boosting overall heat transfer performance. This emphasizes the importance of carefully selecting the size and dimensions of heat exchanger tubes to optimize heat transfer effectiveness and overall efficiency in various industrial applications.
Even though it’s troublesome to manufacture, using austenitic stainless steel seamless tubes for a heat exchange tube can prevent the issues. Since stainless steel seamless tubing has good corrosion resistance and surface, the manufacturing procedure is older, so stainless steel has no Slotted tubes would be the first choice for heat exchange tubes.
specification of Stainless Steel Condenser Tube
| Specifications | ASTM A213, ASTM A249, ASTM A269 |
| Size Range | 6 mm OD to 219.1 mm OD |
| Outside Diameter | From 6mm~2500mm |
| Length | 1 Mtr Upto 32 Mtrs Long / U-Tube Length – 32 Mtrs U Tube Coil – 50 Mtrs |
| Thickness | 0.7 mm Thick To12.7 mm Thick |
| Form | Seamless, Welded, Hot Rolled, Cold Drawn |
| Shapes | Straight tube, Coil tubing |
| Ends | Plain end, Bevelled end |
| Grades | TP – 304,304L,316,316L,201 |
Production Standard of Stainless Steel Condenser Tube
ASME SB-167 ASME SB-423 ASME SB-163 ASME Sb338
ASME SA789 Seamless and Welded Ferrite/Austenitic Stainless Steel Tube for General Use
ASME SA213 Seamless Ferrite and Austenitic Alloy Steel Tube for Boiler, Superheater and Heat Exchanger
ASME SA249 Welded Austenitic Steel Tube for Boiler, Superheater, Heat Exchanger and Condenser Tube
ASME SB-167 ASME SB-423 ASME SB-163 ASME Sb338
ASME SA688 Welded Austenitic Stainless Steel Tube for Feed Water Heater
GB13296 Stainless Steel Seamless Tube for Boiler and Heat Exchanger
Production Range of Stainless Steel Condenser Tube
Normal Pipe Size | Outside Diameter | Normal Wall Thickness (mm) | |||||
NPS | in | BN | mm | SCH5s | SCH10s | SCH40s | SCH80s |
1/8 | 0.405 | 6 | 10.3 | — | 1.24 | 1.73 | 2.41 |
1/4 | 0.540 | 8 | 13.7 | — | 1.65 | 2.24 | 3.02 |
3/8 | 0.675 | 10 | 17.1 | — | 1.65 | 2.31 | 3.2 |
1/2 | 0.840 | 15 | 21.3 | 1.65 | 2.11 | 2.77 | 3.73 |
3/4 | 1.050 | 20 | 26.7 | 1.65 | 2.11 | 2.87 | 3.91 |
1 | 1.315 | 25 | 33.4 | 1.65 | 2.77 | 3.38 | 4.55 |
1 1/4 | 1.660 | 32 | 42.2 | 1.65 | 2.77 | 3.56 | 4.85 |
1 1/2 | 1.900 | 40 | 48.3 | 1.65 | 2.77 | 3.68 | 5.08 |
2 | 2.375 | 50 | 60.3 | 1.65 | 2.77 | 3.91 | 5.54 |
2 1/2 | 2.875 | 65 | 73.0 | 2.11 | 3.05 | 5.16 | 7.01 |
3 | 3.500 | 80 | 88.9 | 2.11 | 3.05 | 5.49 | 7.62 |
3 1/2 | 4.000 | 90 | 101.6 | 2.11 | 3.05 | 5.74 | 8.08 |
4 | 4.500 | 100 | 114.3 | 2.11 | 3.05 | 6.02 | 8.56 |
5 | 5.563 | 125 | 141.3 | 2.77 | 3.4 | 6.55 | 9.53 |
6 | 6.625 | 150 | 168.3 | 2.77 | 3.4 | 7.11 | 10.97 |
8 | 8.625 | 200 | 219.1 | 2.77 | 3.76 | 8.18 | 12.7 |
10 | 10.750 | 250 | 273.1 | 3.4 | 4.19 | 9.27 | 12.7 |
12 | 12.750 | 300 | 323.9 | 3.96 | 4.57 | 9.53 | 12.7 |
14 | 14.000 | 350 | 355.6 | 3.96 | 4.78 | 9.53 | — |
16 | 16.000 | 400 | 406.4 | 4.19 | 4.78 | 9.53 | — |
18 | 18.000 | 450 | 457.2 | 4.19 | 4.78 | 9.53 | — |
20 | 20.000 | 500 | 508.0 | 4.78 | 5.54 | 9.53 | — |
22 | 22.000 | 550 | 558.8 | 4.78 | 5.54 | — | — |
24 | 24.000 | 600 | 609.6 | 5.54 | 6.35 | 9.53 | — |
26 | 26.000 | 650 | 660.4 | — | — | — | — |
28 | 28.000 | 700 | 711.2 | — | — | — | — |
30 | 30.000 | 750 | 762.0 | 6.35 | 7.92 | — | — |
32 | 32.000 | 800 | 812.8 | — | 7.92 | — | — |
34 | 34.000 | 850 | 863.6 | — | 7.92 | — | — |
36 | 36.000 | 900 | 914.4 | — | 7.92 | — | — |
38 | 38.000 | 950 | 965.2 | — | — | — | — |
40 | 40.000 | 1000 | 1016.0 | — | 9.53 | — | — |
If you need more sizes, please consult with us | |||||||
Main grade description in different standard
ASTM | DIN / EN | JIS | GB | ISO Name | Other |
S20100 201 | 1.4372 | SUS201 | S35350 | X12CrMnNiN17–7-5 | J1 L1 LH 201J1 |
S20200 202 | 1.4373 | SUS202 | S35450 | X12CrMnNiN18–9-5 | 202 L4, 202 J4, 202 J3 |
S30400 304 | 1.4301 | SUS304 | S30408 | X5CrNi18-10 | 06Cr19Ni10 0Cr18Ni9 |
S31603 316L | 1.4404 | SUS316L | S31603 | X2CrNiMo17-12-2 | 022Cr17Ni12Mo2 00Cr17Ni14Mo2 |
S40900 409 | – | SUH409 | S11168 | X5CrTi12 | 0Cr11Ti |
S40910 409L | 1.4512 | SUH409L | S11163 | X2CrTi12 | 00Cr11Ti 022Cr11Ti |
S41008 410S | 1.4000 | SUS410S | S11306 | X6Cr13 | – |
S43000 430 | 1.4016 | SUS430 | 10Cr17 | X6Cr17 | 1Cr17 |
Main grade chemical components in different standard
201 | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Mo % |
ASTM | 0.15 | 1.00 | 5.5-7.5 | 0.050 | 0.030 | 3.5-5.5 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.25 | – |
DIN/EN | 0,15 | 1,00 | 5,5-7,5 | 0,045 | 0,015 | 3,5-5,5 | 16,0-18,0 | 0,05-0,25 | – |
JIS | 0.15 | 1.00 | 5.5-7.5 | 0.060 | 0.030 | 3.5-5.5 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.25 | – |
GB | 0.15 | 1.00 | 5.5-7.5 | 0.050 | 0.030 | 3.5-5.5 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.05-0.25 | – |
202 | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Mo % |
ASTM | 0.15 | 1.00 | 7.5-10.0 | 0.060 | 0.030 | 4.0-6.0 | 17.0-19.0 | 0.25 | – |
DIN/EN | 0,15 | 1,00 | 7,5-10,5 | 0,045 | 0,015 | 4,0-6,0 | 17,0-19,0 | 0,05-0,25 | – |
JIS | 0.15 | 1.00 | 7.5-10.0 | 0.060 | 0.030 | 4.0-6.0 | 17.0-19.0 | 0.25 | – |
GB | 0.15 | 1.00 | 7.5-10.0 | 0.050 | 0.030 | 4.0-6.0 | 17.0-19.0 | 0.05-0.25 | – |
304 | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Mo % |
ASTM | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 8.0 – 10.5 | 18.0-20.0 | 0.10 | – |
DIN/EN | 0,07 | 1,00 | 2,00 | 0,045 | 0,015 | 8,0 – 10,5 | 17,5-19,5 | 0,10 | – |
JIS | 0.08 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 8.0 – 10.5 | 18.0-20.0 | – | – |
GB | 0.08 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 8.0 – 10.0 | 18.0-20. 0 | – | – |
316L | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Mo % |
ASTM | 0.030 | 0.75 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 10.0-14.0 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.10 | 2.00-3.00 |
DIN/EN | 0,030 | 1,00 | 2,00 | 0,045 | 0,015 | 10,0-13,0 | 16,5-18,5 | 0,10 | 2,00-2,50 |
JIS | 0.030 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 12.0-15.0 | 16.0-18.0 | – | 2.00-3.00 |
GB | 0.030 | 0.75 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 10.0-14.0 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.10 | 2.00-3.00 |
409 | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Ti % |
ASTM | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 0.50 | 10.5-11.7 | – | 6*C% – 0.75 |
DIN/EN | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
JIS | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.040 | 0.030 | – | 10.5-11.7 | – | 6*C% – 0.75 |
GB | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 0.60 | 10.5-11.7 | – | 6*C% – 0.75 |
409L | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Ti % |
ASTM | 0.03 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.040 | 0.020 | 0.50 | 10.5-11.7 | 0.03 | 6*(C+N)-0.5 |
DIN/EN | 0.03 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.040 | 0.015 | – | 10.5-12.5 | – | 6*(C+N)-0.65 |
JIS | 0.03 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.040 | 0.030 | – | 10.5-11.7 | – | 6*C% – 0.75 |
GB | 0.03 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.040 | 0.020 | – | 10.5-11.7 | 0.03 | Ti≥8*(C+N) |
410S | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Mo % |
ASTM | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.040 | 0.030 | 0.60 | 11.5-13.5 | – | – |
DIN/EN | 0,08 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,040 | 0,015 | – | 12,0-14,0 | – | – |
JIS | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.040 | 0.030 | – | 11.5-13.5 | – | – |
GB | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.040 | 0.030 | 0.60 | 11.5-13.5 | – | – |
Main grade mechanical property in different standard
201 | Y.S./Mpa ≥ | T.S./Mpa ≥ | E.L./% ≥ | HB ≤ | HRB ≤ | HBW ≤ | HV ≤ |
ASTM | 260 | 515 | 40 | – | 95 | 217 | – |
JIS | 275 | 520 | 40 | 241 | 100 | – | 253 |
GB | 205 | 515 | 30 | - | 99 | – | - |
202 | Y.S./Mpa ≥ | T.S./Mpa ≥ | E.L./% ≥ | HB ≤ | HRB ≤ | HBW ≤ | HV ≤ |
ASTM | 260 | 620 | 40 | – | – | 241 | – |
JIS | 275 | 520 | 40 | – | 95 | 207 | 218 |
GB | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
304 | Y.S./Mpa ≥ | T.S./Mpa ≥ | E.L./% ≥ | HB ≤ | HRB ≤ | HBW ≤ | HV ≤ |
ASTM | 205 | 515 | 40 | – | 92 | 201 | – |
JIS | 205 | 520 | 40 | 187 | 90 | – | 200 |
GB | 205 | 515 | 40 | – | 92 | 201 | 210 |
316L | Y.S./Mpa ≥ | T.S./Mpa ≥ | E.L./% ≥ | HB ≤ | HRB ≤ | HBW ≤ | HV ≤ |
ASTM | 170 | 485 | 40 | – | 95 | 217 | – |
JIS | 175 | 480 | 40 | 187 | 90 | 200 | |
GB | 170 | 485 | 40 | – | 95 | 217 | 220 |
409 | Y.S./Mpa ≥ | T.S./Mpa ≥ | E.L./% ≥ | HB ≤ | HRB ≤ | HBW ≤ | HV ≤ |
ASTM | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
JIS | 175 | 360 | 22 | 162 | 80 | – | 175 |
GB | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
409L | Y.S./Mpa ≥ | T.S./Mpa ≥ | E.L./% ≥ | HB ≤ | HRB ≤ | HBW ≤ | HV ≤ |
ASTM | 170 | 380 | 20 | – | 88 | 179 | – |
JIS | 175 | 360 | 25 | 162 | 80 | – | 175 |
GB | 170 | 380 | 20 | – | 88 | 179 | 200 |
410S | Y.S./Mpa ≥ | T.S./Mpa ≥ | E.L./% ≥ | HB ≤ | HRB ≤ | HBW ≤ | HV ≤ |
ASTM | 205 | 415 | 22 | – | 89 | 183 | – |
JIS | 205 | 410 | 20 | – | 88 | 183 | 200 |
GB | 205 | 415 | 20 | – | 89 | 183 | 200 |
characteristics of Stainless Steel Condenser Tube
Heat transfer efficiency is a key characteristic of stainless steel condenser tubes, contributing to their effectiveness in various heat exchange applications. This characteristic refers to the tubes’ ability to efficiently transfer thermal energy between the hot and cold fluids within the condenser system. Several factors contribute to the high heat transfer efficiency of stainless steel condenser tubes:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent thermal conductivity, allowing heat to be rapidly transferred from one fluid to another. This property ensures efficient heat exchange and helps maintain optimal temperature differentials.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, coStainless steel condenser tubes have smooth and polished surfaces that minimize friction and promote laminar flow. This enhances heat transfer by reducing energy losses associated with turbulent flow and fouling.
nsectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Many stainless steel condenser tubes feature thin walls, allowing for a closer proximity between the fluids being exchanged. This proximity maximizes the temperature gradient between the fluids, leading to enhanced heat transfer.
The combination of stainless steel’s thermal conductivity and the tube’s design results in a high heat transfer coefficient. This coefficient represents the rate at which heat is exchanged per unit surface area, ensuring efficient energy transfer.
Stainless steel condenser tubes can maintain efficient heat transfer even under varying operating conditions due to their ability to accommodate a wide range of flow rates and temperatures.
The high heat transfer efficiency of stainless steel tubes allows for the design of compact condenser systems. These systems occupy less space while still delivering the required heat exchange performance.
The smooth surface of stainless steel discourages the accumulation of deposits and fouling, which can degrade heat transfer performance over time.
Depending on the specific alloy used, stainless steel condenser tubes can exhibit varying levels of thermal conductivity, allowing for customization to suit different heat transfer requirements.
Overall, the exceptional heat transfer efficiency of stainless steel condenser tubes ensures that thermal energy is effectively transferred between fluids, promoting efficient processes, reduced energy consumption, and improved overall system performance.
Application of Stainless Steel Condenser Tube
Stainless Steel Condenser Tubes are purposefully crafted to excel at the condensation process, efficiently extracting heat from the exterior of the tube. These tubes find versatile application across different industries. Notably, they play an integral role within the evaporator and condenser phases of refrigeration cycles in chillers, offering reliable cooling solutions. In addition, they contribute to the condensation of steam within surface condensers and are crucial components of heat exchangers.
Constructed from resilient, corrosion-resistant materials, stainless steel condenser tubes guarantee longevity even when subjected to corrosive condensing fluids. Their remarkable mechanical strength further safeguards against potential tube deterioration arising from continuous contact with these fluids. This durability ensures consistent performance and extended operational lifespans, making them indispensable for efficient heat transfer processes.
Stainless Steel Condenser Tubes stand as a testament to engineering precision, designed to optimize heat exchange efficiency and enhance overall system productivity. Their ability to swiftly and effectively dissipate thermal energy underscores their significance across various sectors, where reliable condensation is vital for effective operations.
FAQ
Stainless steel condenser tubes are used to efficiently extract heat from a fluid and condense it into a liquid state. The major uses of these tubes include:
- Refrigeration and air-conditioning systems: Stainless steel condenser tubes are commonly used in refrigeration and air-conditioning systems to extract heat from air or other media, cool it down to a liquid state, and then discharge it through pipes.
- Heat exchangers: In heat exchangers, stainless steel condenser tubes are used to transfer heat from one fluid to another for efficient energy transfer, commonly used in the chemical, power and process industries.
- Turbines and Power Plants: Stainless steel condenser tubes are used in turbines and power plants to cool high-temperature, high-pressure vapors into a liquid for re-circulation.
- Industrial Processes: Stainless steel condenser tubes are used to cool and condense fluids to maintain process stability in a variety of industrial processes, such as chemical production, petroleum refining and food processing.
- Energy production: In nuclear power plants, petroleum refineries and chemical plants, stainless steel condenser tubes are used to cool and condense fluids to ensure the safe and efficient operation of equipment.
- Ice machines: Stainless steel condenser tubes are used in ice machines to cool and condense vapors, converting them to a liquid state.
In short, stainless steel condenser tubes play a critical role in many industries to control temperatures, cool fluids and keep systems running properly.
Stainless Steel Condenser Tubes take a variety of steps in improving heat transfer efficiency to ensure an efficient heat transfer and condensation process. The role of stainless steel pipe suppliers in the material selection and manufacturing process is critical.
- Quality Material Selection: Stainless steel condenser tubes are typically manufactured from stainless steel materials with excellent corrosion resistance, such as 316/316L stainless steel, to ensure excellent performance in a variety of environments without corrosion.
- Design of internal and external surfaces: The design and finish of the internal and external surfaces of the tubes affect the heat transfer efficiency. Fine surface finishes and optimized geometries can provide greater surface area for heat exchange and promote faster heat transfer.
- Spiral Texturing and Reinforcements: Some stainless steel condenser tubes are designed with spiral texturing or reinforcements to increase the contact area between the fluid and the tube wall, thereby improving heat transfer efficiency.
- Fluid Velocity and Turbulence: By controlling fluid velocity and introducing turbulence, the heat exchange between the fluid and the tube wall can be enhanced to improve heat transfer efficiency.
- Efficient Manufacturing Processes: During the manufacturing process, advanced technologies and processes are used to ensure the flatness and smoothness of the inner and outer surfaces of the pipe, reducing the resistance to fluid flow and thus improving the heat transfer efficiency.
The expertise and contribution of stainless steel pipe suppliers in material selection and manufacturing processes are essential to ensure the efficient performance and heat transfer efficiency of stainless steel condenser tubes.
The material used for Stainless Steel Condenser Tubes is typically high-quality stainless steel, such as 316/316L stainless steel, known for its excellent corrosion resistance and durability. These tubes are carefully selected and supplied by reputable stainless steel pipe suppliers to ensure optimal performance in condensation processes. The choice of stainless steel material is crucial to prevent corrosion and ensure long-term efficiency in various condensation applications.
Maintaining Stainless Steel Condenser Tubes involves several key steps to ensure their optimal performance and longevity. Reputable stainless steel pipe suppliers often provide guidelines for proper maintenance. Here are essential maintenance practices:
- Regular Cleaning: Periodically clean the tubes to remove debris, deposits, and fouling that can hinder heat transfer efficiency. Use appropriate cleaning solutions and methods recommended by stainless steel pipe suppliers.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect the tubes for signs of corrosion, pitting, or damage. Early detection can prevent more significant issues and extend the tube’s lifespan.
- Corrosion Prevention: Apply suitable protective coatings or inhibitors to minimize the risk of corrosion. Stainless steel’s inherent corrosion resistance is an advantage, but additional measures can enhance its durability.
- Fluid Quality: Ensure the quality of the process fluid used in the condensation system. Impurities or corrosive substances in the fluid can negatively impact the tubes’ condition.
- Maintenance Schedule: Follow a maintenance schedule provided by stainless steel pipe suppliers or industry standards. Regular maintenance can prevent unexpected downtime and optimize performance.
- Tube Support: Ensure proper support and alignment of the tubes to avoid stress and damage caused by vibrations or thermal expansion.
- Professional Inspection: Periodically involve experts to conduct thorough inspections and assessments of the tubes’ condition. This can identify potential issues early and allow for timely corrective actions.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of maintenance activities, inspection reports, and any repairs performed. This information can aid in tracking the tubes’ performance over time.
By adhering to these maintenance practices and seeking guidance from reliable stainless steel pipe suppliers, you can ensure the efficient and reliable operation of your Stainless Steel Condenser Tubes in various applications.
Yes, Stainless Steel Condenser Tubes are designed to operate effectively under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions. They are typically manufactured from corrosion-resistant stainless steel alloys, chosen for their ability to withstand extreme environments. Reputable stainless steel pipe suppliers offer tubes with suitable material properties to handle the elevated pressures and temperatures often encountered in condensation processes. These tubes maintain their structural integrity, thermal conductivity, and resistance to corrosion even in demanding applications, ensuring reliable performance in diverse industrial settings.
The pricing of Stainless Steel Condenser Tubes can vary based on factors such as material grade, size, quantity, and market conditions. Huaxiao Stainless Steel, a reputable supplier, offers competitive pricing for high-quality condenser tubes. It’s recommended to contact Huaxiao stainless steel pipe suppliers directly to get accurate and up-to-date pricing information tailored to your specific requirements. Their experienced team can provide quotes and assist with selecting the right condenser tubes that fit your budget and application needs.
Other Products
Get In touch
Ready to Elevate Your Projects? Dive into our Stainless Steel Collection and Submit Your Specifications Today!
Phone/WhatsApp/WeChat:
+86 13052085117
Email: [email protected]
Address: RM557, NO.1388 Jiangyue Road, Shanghai China