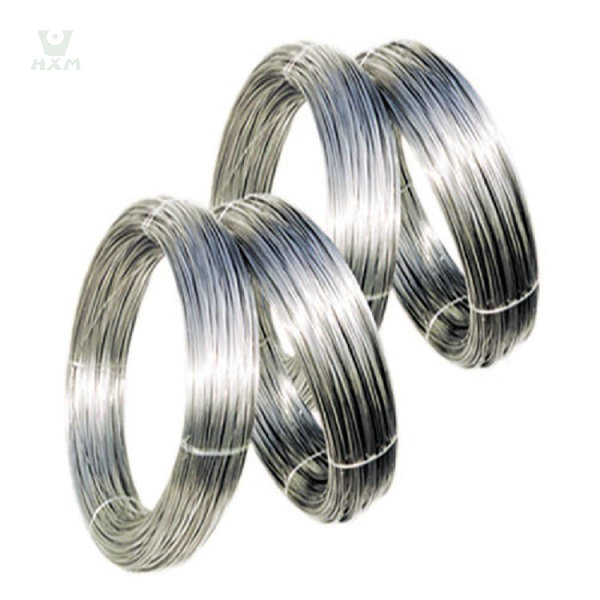
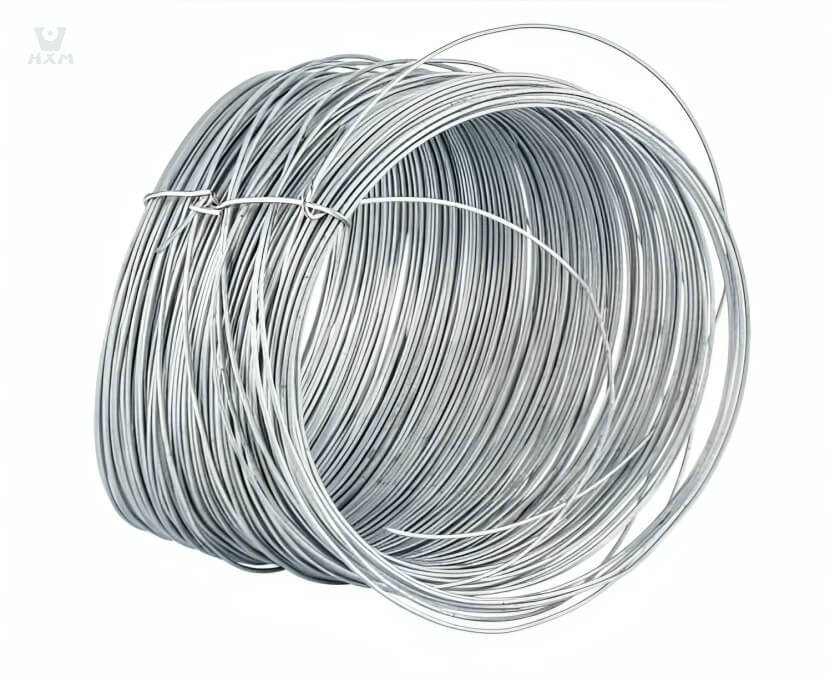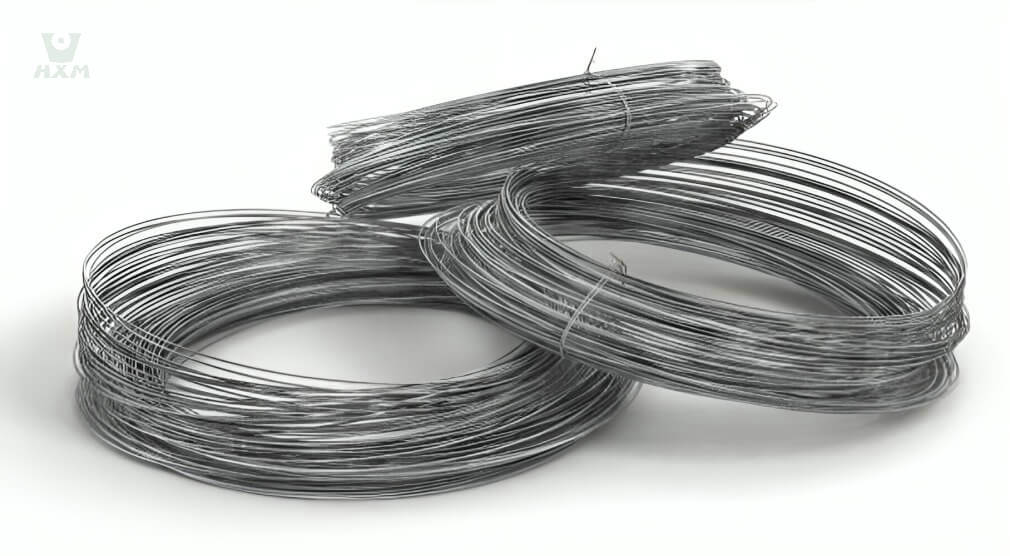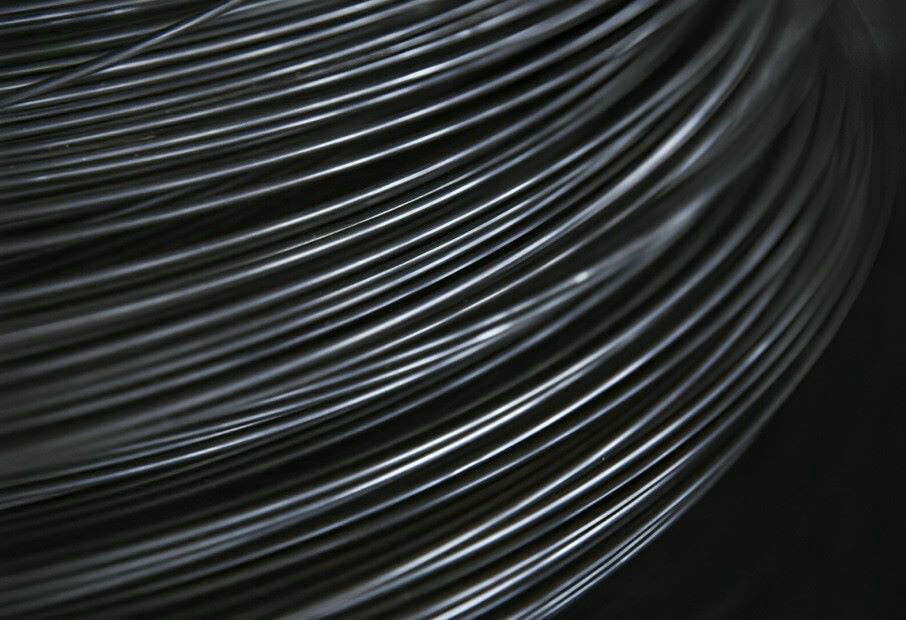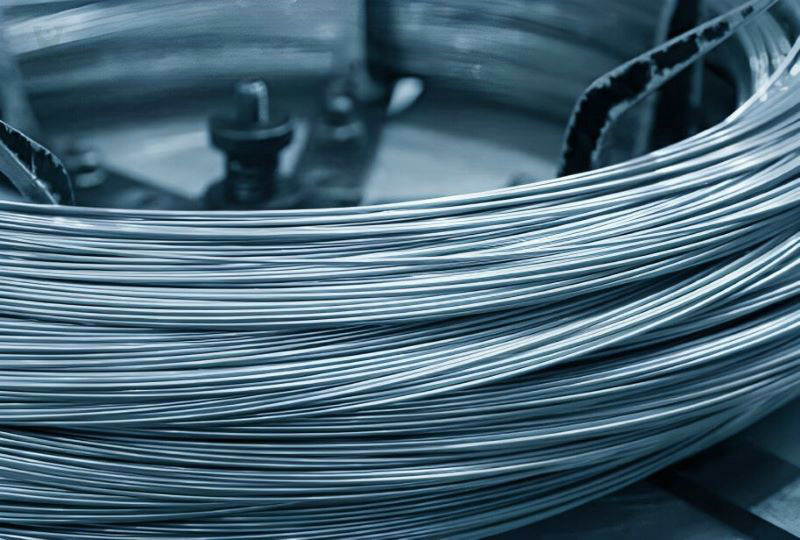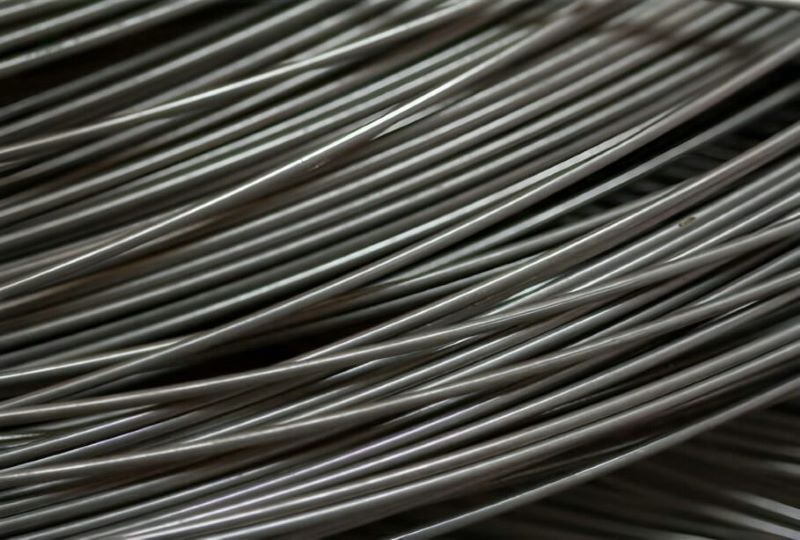
Bright stainless steel wire supplier in China
Size: Diameter 0.2mm-5.5mm, 5.5mm-12mm
Standard: GB1220, ASTM A 484/484M, EN 10060/ DIN 1013 ASTM A276, EN 10278, DIN 671
Main Grade: 201, 304, 316, 316L, 310s, 409, 430
Finish: Black, NO.1, mill finish, cold draw
Product Description of Bright stainless steel wire
Our Bright Stainless Steel Wire epitomizes excellence, boasting unparalleled qualities in the realm of stainless steel products. Crafted meticulously from top-grade alloys, this wire embodies exceptional resistance to corrosion, high temperatures, and exhibits superior low-temperature strength. It excels in mechanical properties, enabling effortless stamping, bending, and retains its inherent hardness without the need for heat therapy.
With a visually stunning surface condition, it offers outstanding formability, ensuring uniform elasticity and high plasticity. Notably, it possesses exceptional straightening capabilities, broad elasticity range, and facilitates easy automatic winding due to its uniform wire diameter.
Packaging options for bright stainless steel wire range from reels, spools, trays to wooden crates, catering to diverse requirements. The product’s flawlessly smooth surface devoid of any cracks ensures utmost safety in use. Rigorous adherence to standardized raw materials and stringent quality control measures during production substantiate its consistent quality.
Our Bright Stainless Steel Wire stands as a testament to precision engineering, ensuring a striking balance between exceptional quality, reliable performance, and enduring durability across diverse applications.
specification of Bright stainless steel wire
production range of bright stainless steel wire
Size: Diameter 0.2mm-5.5mm, 5.5mm-12mm
Standard: GB1220, ASTM A484/484M, EN 10060/ DIN 1013 ASTM A276, EN 10278, DIN 671
Main Grade: 201, 304, 316, 316L, 310s, 430
Finish: Black, NO.1, mill finish, cold draw
chemical composition of bright stainless steel wire
201 | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Mo % |
ASTM | 0.15 | 1.00 | 5.5-7.5 | 0.050 | 0.030 | 3.5-5.5 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.25 | – |
DIN/EN | 0,15 | 1,00 | 5,5-7,5 | 0,045 | 0,015 | 3,5-5,5 | 16,0-18,0 | 0,05-0,25 | – |
JIS | 0.15 | 1.00 | 5.5-7.5 | 0.060 | 0.030 | 3.5-5.5 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.25 | – |
GB | 0.15 | 1.00 | 5.5-7.5 | 0.050 | 0.030 | 3.5-5.5 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.05-0.25 | – |
202 | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Mo % |
ASTM | 0.15 | 1.00 | 7.5-10.0 | 0.060 | 0.030 | 4.0-6.0 | 17.0-19.0 | 0.25 | – |
DIN/EN | 0,15 | 1,00 | 7,5-10,5 | 0,045 | 0,015 | 4,0-6,0 | 17,0-19,0 | 0,05-0,25 | – |
JIS | 0.15 | 1.00 | 7.5-10.0 | 0.060 | 0.030 | 4.0-6.0 | 17.0-19.0 | 0.25 | – |
GB | 0.15 | 1.00 | 7.5-10.0 | 0.050 | 0.030 | 4.0-6.0 | 17.0-19.0 | 0.05-0.25 | – |
304 | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Mo % |
ASTM | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 8.0 – 10.5 | 18.0-20.0 | 0.10 | – |
DIN/EN | 0,07 | 1,00 | 2,00 | 0,045 | 0,015 | 8,0 – 10,5 | 17,5-19,5 | 0,10 | – |
JIS | 0.08 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 8.0 – 10.5 | 18.0-20.0 | – | – |
GB | 0.08 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 8.0 – 10.0 | 18.0-20. 0 | – | – |
316L | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Mo % |
ASTM | 0.030 | 0.75 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 10.0-14.0 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.10 | 2.00-3.00 |
DIN/EN | 0,030 | 1,00 | 2,00 | 0,045 | 0,015 | 10,0-13,0 | 16,5-18,5 | 0,10 | 2,00-2,50 |
JIS | 0.030 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 12.0-15.0 | 16.0-18.0 | – | 2.00-3.00 |
GB | 0.030 | 0.75 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 10.0-14.0 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.10 | 2.00-3.00 |
409 | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Ti % |
ASTM | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 0.50 | 10.5-11.7 | – | 6*C% – 0.75 |
DIN/EN | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
JIS | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.040 | 0.030 | – | 10.5-11.7 | – | 6*C% – 0.75 |
GB | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 0.60 | 10.5-11.7 | – | 6*C% – 0.75 |
310s | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Mo % |
ASTM | 0.08 | 1.50 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 19.0-22.0 | 24.0-26.0 | – | – |
DIN/EN | 0,10 | 1,50 | 2,00 | 0,045 | 0,015 | 19,0-22,0 | 24,0-26,0 | 0,10 | – |
JIS | 0.08 | 1.50 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 19.0-22.0 | 24.0-26.0 | – | – |
GB | 0.08 | 1.50 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 19.0-22.0 | 24.0-26.0 | – | – |
410S | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Mo % |
ASTM | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.040 | 0.030 | 0.60 | 11.5-13.5 | – | – |
DIN/EN | 0,08 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,040 | 0,015 | – | 12,0-14,0 | – | – |
JIS | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.040 | 0.030 | – | 11.5-13.5 | – | – |
GB | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.040 | 0.030 | 0.60 | 11.5-13.5 | – | – |
features of Bright stainless steel wire
This attribute is primarily attributed to the wire’s surface finishing process, typically involving mechanical or chemical treatments. The surface quality is a result of meticulous polishing, which creates a microscopically smooth and uniform surface texture. The polishing process involves abrasives or chemical agents that remove surface irregularities, imperfections, and oxides, resulting in a reflective and visually appealing appearance.
At a microscopic level, this polished surface exhibits a reduced roughness average (Ra), indicating fewer microscopic peaks and valleys on the wire’s surface. The reduction of surface irregularities enhances light reflection, giving the wire its characteristic luster and brilliance.
Moreover, this polished surface enhances the wire’s resistance to corrosion by minimizing areas where contaminants or corrosive agents could adhere. The smoother surface decreases the likelihood of corrosion initiation points, thus augmenting the wire’s overall longevity and durability in various environments.
The high-quality shiny surface of Bright Stainless Steel Wire not only contributes to its aesthetic appeal but also serves functional purposes by improving its resistance to corrosion, ease of cleaning, and suitability for applications where a visually attractive appearance is essential.
Formability refers to the wire’s capability to undergo plastic deformation without experiencing structural damage or failure. This characteristic is a result of the wire’s inherent microstructural properties and composition.
The crystalline structure of stainless steel wire, typically austenitic or a combination of austenitic and ferritic phases, contributes significantly to its formability. The arrangement of atoms in these structures allows for deformation mechanisms, such as slip and twinning, which enable the wire to undergo shaping processes.
The wire’s metallurgical properties, including grain size, distribution, and orientation, play a pivotal role in determining its formability. Smaller and uniformly distributed grains provide increased ductility, allowing the wire to easily conform to various shapes and bends without fracturing or losing its integrity.
Additionally, the wire’s chemical composition, especially the percentage of alloying elements like chromium, nickel, and manganese, influences its malleability. These elements contribute to the wire’s solid solution strengthening, enhancing its ability to deform plastically without undergoing failure.
During manufacturing, processes such as drawing, rolling, or annealing are utilized to optimize the wire’s microstructure and enhance its formability. These processes align the crystallographic orientation, refine the grain structure, and relieve internal stresses, thereby improving the wire’s capacity to be shaped or formed according to specific requirements.
Bright Stainless Steel Wire’s excellent formability allows it to be easily manipulated into desired shapes, facilitating various manufacturing processes such as bending, stamping, and machining. Its ability to maintain structural integrity during deformation makes it a preferred material for applications requiring intricate shapes or customized designs.
Weldability refers to the wire’s ability to be joined efficiently and effectively through welding processes without detrimental effects on its integrity or properties. Several inherent metallurgical and compositional factors contribute to the exceptional weldability of this wire.
The microstructure of stainless steel wire, often consisting of austenitic or duplex phases, plays a crucial role in its weldability. These structures offer a favorable balance between alloying elements, providing a stable matrix that promotes the formation of a robust weld joint.
The presence of alloying elements like chromium, nickel, and molybdenum in the wire’s composition significantly influences its weldability. Chromium forms a passive oxide layer, preventing corrosion and maintaining stability during the welding process. Nickel enhances ductility and toughness, reducing the susceptibility to cracking. Molybdenum contributes to improved resistance to pitting corrosion and aids in maintaining structural integrity during welding.
The wire’s low carbon content helps mitigate the formation of undesirable carbides, which can lead to weld embrittlement. Additionally, specific heat treatments or annealing processes can be employed to further refine the microstructure, reducing residual stresses and enhancing the wire’s weldability.
During welding, the wire exhibits minimal heat-affected zones due to its controlled thermal conductivity and heat dissipation properties. This characteristic minimizes the risk of distortion, cracks, or structural changes in the surrounding areas, ensuring the integrity of the welded joint.
Bright Stainless Steel Wire’s excellent weldability facilitates seamless and robust joining, enabling it to be effectively integrated into various fabrication processes. Its weldability ensures strong and reliable connections, making it a preferred material for applications where welding plays a pivotal role in assembly or construction processes.
Stainless steel wire’s magnetic behavior primarily depends on its microstructural composition and phase balance. Austenitic stainless steels, commonly used in this wire, typically exhibit weak magnetic properties due to their specific atomic arrangement.
In the austenitic phase, stainless steel’s atomic structure contains a high amount of chromium and nickel, which are crucial alloying elements. These elements tend to form a face-centered cubic (FCC) crystal lattice structure, which inherently imparts weak ferromagnetic properties to the material.
The presence of these elements, particularly nickel, influences the formation of the non-magnetic austenitic phase. Nickel disrupts the magnetic domains within the material, resulting in reduced magnetic susceptibility. Additionally, the high chromium content forms a protective oxide layer on the surface, further diminishing magnetic permeability.
The wire’s weak magnetic properties are also attributed to its grain structure and crystallographic arrangement. Austenitic stainless steels tend to form randomly oriented grains, minimizing the alignment of magnetic domains and subsequently weakening the overall magnetic behavior.
The weak magnetic properties of Bright Stainless Steel Wire make it suitable for applications where magnetic interference needs to be minimized or eliminated. Industries such as electronics, medical devices, and environments sensitive to magnetic fields benefit from the wire’s reduced magnetic susceptibility, ensuring minimal impact on surrounding equipment or processes that are sensitive to magnetic influences.
These features collectively underscore the versatility, adaptability, and reliability of Bright Stainless Steel Wire, making it a preferred choice across diverse industries such as automotive, medical, electronics, and more. Its combination of visual appeal, malleability, weldability, and reduced magnetic properties contributes significantly to its widespread applications and functional versatility.
application of Bright stainless steel wire
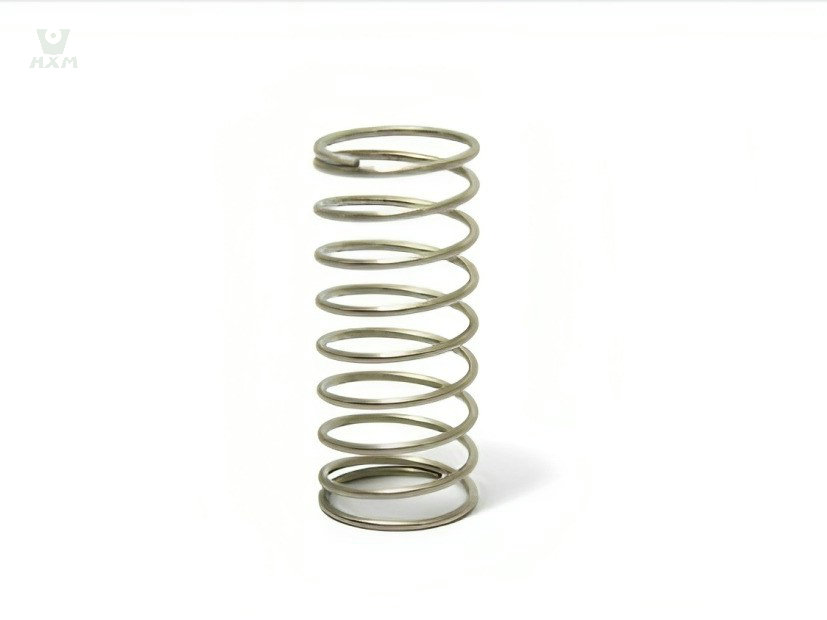
The distinction between soft and hard variants allows for tailored usage in diverse applications. Soft wire is often utilized in basket weaving, crafting, and as tie wires in construction. Hard wire finds application in more demanding environments, such as industrial tools, machinery components, and springs requiring higher tensile strength.
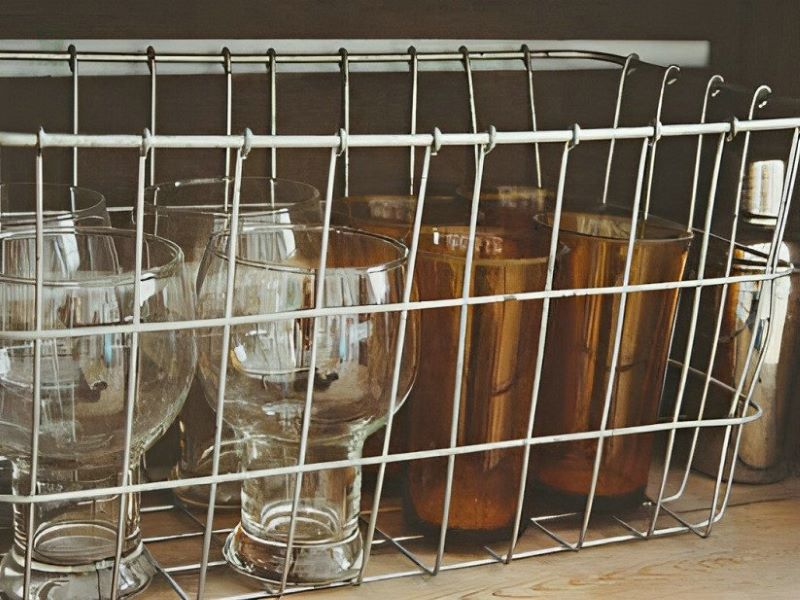

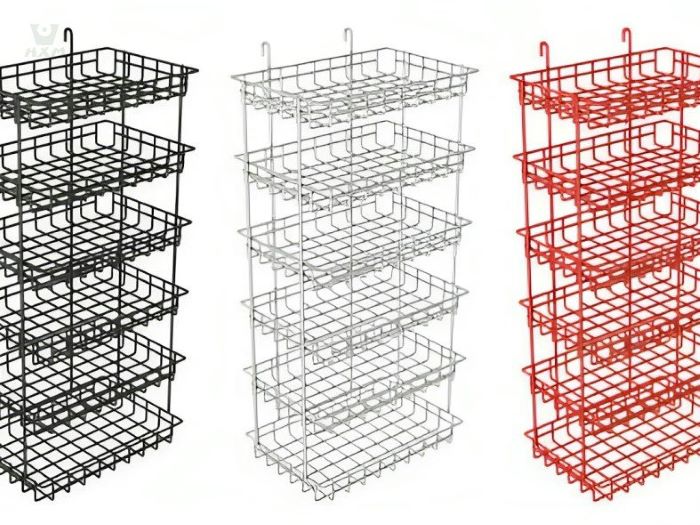



- Baskets: Bright Stainless Steel Wire is extensively employed in crafting various types of baskets due to its corrosion resistance, durability, and aesthetic appeal. These baskets find use in kitchenware, storage solutions, and decorative items.
- Household Items: Its versatility makes Bright Stainless Steel Wire a material of choice for manufacturing a wide array of household items. It's used in producing kitchen utensils, dish racks, wire shelves, clothing hangers, and other domestic essentials due to its hygienic properties and durability.
- Industrial Tools: Hard bright stainless steel wire is employed in the fabrication of industrial tools and machinery components due to its excellent strength and resistance to wear. It's utilized in the construction of cutting tools, springs, fasteners, and precision components requiring high tensile strength and durability in harsh industrial environments.
Bright Stainless Steel Wire’s adaptability to different hardness levels enables its use in a myriad of applications across domestic, industrial, and artisanal sectors, showcasing its versatility and reliability in diverse environments.
FAQ
The manufacturing process of bright stainless steel wire involves a series of precise and controlled steps, ensuring the production of a high-quality, visually appealing, and durable product. Stainless steel wire manufacturers employ advanced techniques and machinery for this purpose.
Selection of Raw Materials:
- The process begins with the careful selection of high-grade stainless steel raw materials. Manufacturers typically use austenitic stainless steel alloys such as 304 or 316 due to their corrosion resistance and formability.
Melting and Casting:
- The chosen stainless steel materials are melted in an electric arc furnace or an induction furnace. Once molten, the steel is cast into large ingots or continuous casting molds to form billets.
Hot Rolling:
- The billets are then heated and hot rolled into thin rods or wires of various diameters. This process involves passing the material through a series of rollers, gradually reducing its thickness while maintaining its length.
Annealing:
- The hot-rolled wire undergoes annealing, a crucial step that involves heating the wire to specific temperatures and controlled cooling. Annealing relieves internal stresses, softens the material, and refines its microstructure, enhancing its formability and machinability.
Pickling and Descaling:
- The annealed wire is then subjected to pickling and descaling processes to remove surface impurities, oxides, and any remaining scale resulting from the hot rolling stage. This step ensures a clean and smooth surface finish.
Cold Drawing or Cold Heading:
- The wire is further processed through cold drawing or cold heading processes, wherein the wire is pulled through a series of dies or molds to achieve the desired diameter and shape. This cold working process enhances the wire’s mechanical properties, precision, and surface finish.
Bright Annealing and Polishing:
- For producing bright stainless steel wire, a final stage involves bright annealing, a controlled heat treatment process performed in a controlled atmosphere. This step optimizes the wire’s surface finish, brightness, and removes any residual stresses. Polishing may follow, enhancing its aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance.
Quality Control and Packaging:
- Throughout the manufacturing process, stainless steel wire manufacturers implement rigorous quality control measures to ensure consistent quality. Finally, the finished bright stainless steel wire is packaged according to industry standards for safe transportation and storage.
Stainless steel wire manufacturers meticulously adhere to these manufacturing steps, leveraging advanced technology and quality assurance protocols to produce bright stainless steel wire with superior mechanical properties, surface finish, and corrosion resistance for a myriad of industrial applications.
Bright Stainless Steel Wire differs from other types of stainless steel wire due to its specific characteristics and finishing process, setting it apart in various applications. When compared to other stainless steel wires, the distinguishing features of Bright Stainless Steel Wire include:
Surface Finish:
- The primary distinction lies in its surface finish. Bright Stainless Steel Wire undergoes a specialized finishing process that imparts a smooth, reflective, and lustrous surface appearance. This unique finishing method ensures a visually appealing and polished look, distinguishing it from standard stainless steel wire types.
Aesthetic Appeal:
- The specialized surface treatment of Bright Stainless Steel Wire enhances its aesthetic appeal, making it highly desirable for decorative purposes. This wire type is often sought after in architectural, interior design, and decorative applications due to its attractive appearance.
Applications:
- Bright Stainless Steel Wire is commonly preferred for applications where aesthetics play a significant role. It finds extensive use in decorative elements, architectural cladding, interior fittings, and artistic installations. Unlike standard stainless steel wire, which is more commonly used in industrial applications, Bright Stainless Steel Wire is specifically tailored for decorative purposes.
Specialized Manufacturers:
- The procurement of Bright Stainless Steel Wire is often associated with specialized stainless steel wire manufacturers who cater to artistic and design-focused markets. These suppliers offer a range of decorative stainless steel products, including sheets, wires, and other architectural elements, tailored to meet aesthetic demands.
Surface Treatment Process:
- Bright Stainless Steel Wire undergoes additional surface treatment processes such as bright annealing and polishing to achieve its distinctive appearance. This process enhances its corrosion resistance, durability, and overall visual appeal, setting it apart from standard stainless steel wire types.
In summary, the key differences of Bright Stainless Steel Wire from other types of stainless steel wire lie in its specialized surface finish, aesthetic appeal, targeted applications in decorative and architectural sectors, and association with specialized suppliers catering to decorative stainless steel products. These distinctive features make it an ideal choice for design-oriented applications, separating it from the more utilitarian uses of standard stainless steel wire.
Weldability refers to the wire’s ability to be joined efficiently and effectively through welding processes without detrimental effects on its integrity or properties. Several inherent metallurgical and compositional factors contribute to the exceptional weldability of this wire.
The microstructure of stainless steel wire, often consisting of austenitic or duplex phases, plays a crucial role in its weldability. These structures offer a favorable balance between alloying elements, providing a stable matrix that promotes the formation of a robust weld joint.
The presence of alloying elements like chromium, nickel, and molybdenum in the wire’s composition significantly influences its weldability. Chromium forms a passive oxide layer, preventing corrosion and maintaining stability during the welding process. Nickel enhances ductility and toughness, reducing the susceptibility to cracking. Molybdenum contributes to improved resistance to pitting corrosion and aids in maintaining structural integrity during welding.
The wire’s low carbon content helps mitigate the formation of undesirable carbides, which can lead to weld embrittlement. Additionally, specific heat treatments or annealing processes can be employed to further refine the microstructure, reducing residual stresses and enhancing the wire’s weldability.
During welding, the wire exhibits minimal heat-affected zones due to its controlled thermal conductivity and heat dissipation properties. This characteristic minimizes the risk of distortion, cracks, or structural changes in the surrounding areas, ensuring the integrity of the welded joint.
Bright Stainless Steel Wire’s excellent weldability facilitates seamless and robust joining, enabling it to be effectively integrated into various fabrication processes. Its weldability ensures strong and reliable connections, making it a preferred material for applications where welding plays a pivotal role in assembly or construction processes.
The selection between hard or soft Bright Stainless Steel Wire depends on the specific application requirements and desired characteristics. Stainless steel wire manufacturers may recommend using either hard or soft wire based on the following situations:
Hard Bright Stainless Steel Wire:
Applications Requiring Strength: Use hard wire when applications demand higher tensile strength, durability, or structural integrity. It is suitable for industrial uses, heavy-duty construction, or applications where the wire needs to withstand significant stress or load-bearing requirements.
Spring Manufacturing: Hard stainless steel wire is commonly employed in spring manufacturing, especially for applications where a stronger and more rigid spring is necessary, such as automotive, machinery components, or industrial tools.
Soft Bright Stainless Steel Wire:
Artistic and Decorative Applications: Soft wire is preferable for artistic and decorative applications, especially in architectural or interior design projects. It is more malleable and easier to shape, making it ideal for creating intricate designs, decorative elements, or ornamental fixtures.
Craftsmanship and DIY Projects: Soft wire is suitable for various crafting projects, DIY endeavors, or hobbies where ease of manipulation and bending is essential. It can be easily shaped or formed without requiring significant force or specialized tools.
In summary, stainless steel wire manufacturers might recommend using hard wire for applications demanding strength and durability, such as industrial uses or spring manufacturing. Conversely, soft wire is suitable for artistic, decorative, or crafting purposes that require malleability and ease of shaping. The supplier’s expertise can guide users in selecting the appropriate wire type based on the intended use and specific project requirements.
The price and cost of Bright Stainless Steel Wire can vary depending on several factors, including the supplier, quality, grade of stainless steel, and the specific finishing processes involved. Comparatively, when evaluated against alternative materials, stainless steel wire manufacturers might provide insights into the following considerations:
Initial Cost:
Bright Stainless Steel Wire may have a higher initial cost compared to some alternative materials. However, its long-term value often outweighs the initial expense due to its durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal.
Durability and Longevity:
While the upfront cost of Bright Stainless Steel Wire might be higher than certain alternatives, its durability and resistance to corrosion often result in lower maintenance and replacement costs over time. This factor contributes to its cost-effectiveness in the long run.
Comparative Maintenance Expenses:
Stainless steel’s minimal maintenance requirements, especially in terms of corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning, can reduce ongoing maintenance expenses compared to materials requiring frequent upkeep or replacements.
Life Cycle Cost Analysis:
A comprehensive life cycle cost analysis might demonstrate that while the initial purchase cost of Bright Stainless Steel Wire may be higher, its extended lifespan and reduced maintenance expenses make it a cost-effective choice in the long term.
Value and Aesthetic Appeal:
Bright Stainless Steel Wire’s premium appearance and aesthetic value add an intrinsic worth to applications such as architectural or decorative projects. Its ability to enhance visual appeal can justify the slightly higher initial cost compared to alternatives.
Overall, stainless steel wire manufacturers may highlight that while Bright Stainless Steel Wire might have a higher initial price compared to certain alternatives, its durability, longevity, low maintenance requirements, and aesthetic value contribute to its cost-effectiveness and overall value proposition in various applications. Evaluating the total cost of ownership over the product’s life cycle can demonstrate its economic advantages despite the initial investment.
Get In touch
Ready to Elevate Your Projects? Dive into our Stainless Steel Collection and Submit Your Specifications Today!
Phone/WhatsApp/WeChat:
+86 13052085117
Email: [email protected]
Address: RM557, NO.1388 Jiangyue Road, Shanghai China









