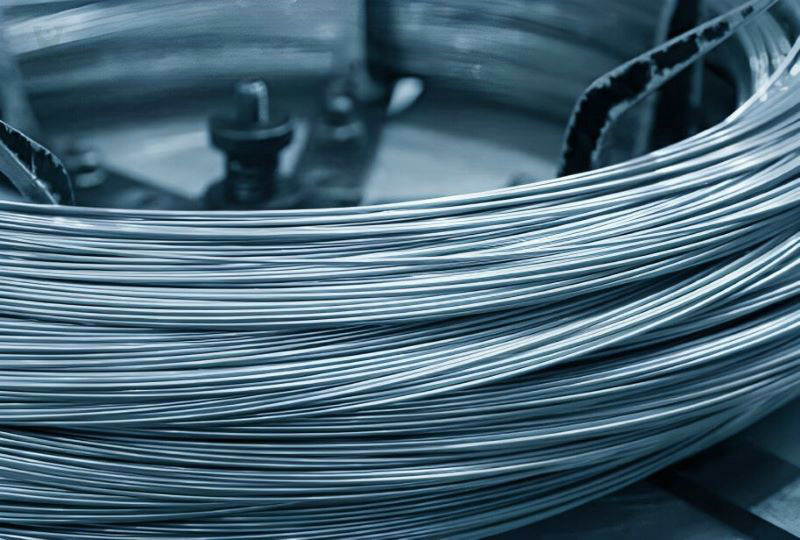
Stainless Steel Wire Screw Supplier
Size: Diameter 0.2mm-5.5mm, 5.5mm-12mm
Standard: GB1220, ASTM A484/484M, EN 10060/ DIN 1013 ASTM A276, EN 10278, DIN 671
Main Grade: 201, 304, 316, 316L, 310s, 430
Finish: Black, NO.1, mill finish, cold draw
Product Description of Stainless steel wire screw
Stainless Steel Wire Screw, designed to enhance fastening technology and connection reliability. Crafted from high-quality stainless steel, this wire screw sleeve excels in corrosive environments while offering exceptional durability. Its inherent elasticity ensures even load distribution, eliminating pitch and tooth type deviations. As a result, connection strength and resistance to vibrations are significantly improved. The locking mechanism secures the screw within the threaded hole, preventing loosening due to shock vibrations. With superior hardness, this wire screw offers extended reusability.
Beyond its inherent properties, the wire screw sleeve improves connection performance by mitigating issues like sliding wire and wrong tooth engagement. This product adheres to quality and performance standards associated with stainless steel cold forging cables, making it suitable for various mechanical components and electronic devices. Its application involves anti-corrosion and mechanical properties tailored to the specific materials used. The selection of higher quality materials during cold forging ensures better formability. Furthermore, it is manufactured by Huaxiao Stainless Steel Wire Manufactures, providing further assurance of its reliability and quality.
specification of Stainless steel wire screw
Production Range of Stainless steel wire screw
Size: Diameter 0.2mm-5.5mm, 5.5mm-12mm
Standard: GB1220, ASTM A484/484M, EN 10060/ DIN 1013 ASTM A276, EN 10278, DIN 671
Main Grade: 201, 304, 316, 316L, 310s, 430
Finish: Black, NO.1, mill finish, cold draw
Main grade description in different standard
ASTM | DIN / EN | JIS | GB | ISO Name | Other |
S20100 201 | 1.4372 | SUS201 | S35350 | X12CrMnNiN17–7-5 | J1 L1 LH 201J1 |
S20200 202 | 1.4373 | SUS202 | S35450 | X12CrMnNiN18–9-5 | 202 L4, 202 J4, 202 J3 |
S30400 304 | 1.4301 | SUS304 | S30408 | X5CrNi18-10 | 06Cr19Ni10 0Cr18Ni9 |
S31603 316L | 1.4404 | SUS316L | S31603 | X2CrNiMo17-12-2 | 022Cr17Ni12Mo2 00Cr17Ni14Mo2 |
S40900 409 | – | SUH409 | S11168 | X5CrTi12 | 0Cr11Ti |
S31008 310S | 1.4951 | SUS310S | S31008 | X12CrNi23-12 | 06Cr25Ni20 0Cr25Ni20 |
S41008 410S | 1.4000 | SUS410S | S11306 | X6Cr13 | – |
S43000 430 | 1.4016 | SUS430 | 10Cr17 | X6Cr17 | 1Cr17 |
Main grade chemical components in different standard
201 | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Mo % |
ASTM | 0.15 | 1.00 | 5.5-7.5 | 0.050 | 0.030 | 3.5-5.5 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.25 | – |
DIN/EN | 0,15 | 1,00 | 5,5-7,5 | 0,045 | 0,015 | 3,5-5,5 | 16,0-18,0 | 0,05-0,25 | – |
JIS | 0.15 | 1.00 | 5.5-7.5 | 0.060 | 0.030 | 3.5-5.5 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.25 | – |
GB | 0.15 | 1.00 | 5.5-7.5 | 0.050 | 0.030 | 3.5-5.5 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.05-0.25 | – |
202 | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Mo % |
ASTM | 0.15 | 1.00 | 7.5-10.0 | 0.060 | 0.030 | 4.0-6.0 | 17.0-19.0 | 0.25 | – |
DIN/EN | 0,15 | 1,00 | 7,5-10,5 | 0,045 | 0,015 | 4,0-6,0 | 17,0-19,0 | 0,05-0,25 | – |
JIS | 0.15 | 1.00 | 7.5-10.0 | 0.060 | 0.030 | 4.0-6.0 | 17.0-19.0 | 0.25 | – |
GB | 0.15 | 1.00 | 7.5-10.0 | 0.050 | 0.030 | 4.0-6.0 | 17.0-19.0 | 0.05-0.25 | – |
304 | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Mo % |
ASTM | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 8.0 – 10.5 | 18.0-20.0 | 0.10 | – |
DIN/EN | 0,07 | 1,00 | 2,00 | 0,045 | 0,015 | 8,0 – 10,5 | 17,5-19,5 | 0,10 | – |
JIS | 0.08 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 8.0 – 10.5 | 18.0-20.0 | – | – |
GB | 0.08 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 8.0 – 10.0 | 18.0-20. 0 | – | – |
316L | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Mo % |
ASTM | 0.030 | 0.75 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 10.0-14.0 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.10 | 2.00-3.00 |
DIN/EN | 0,030 | 1,00 | 2,00 | 0,045 | 0,015 | 10,0-13,0 | 16,5-18,5 | 0,10 | 2,00-2,50 |
JIS | 0.030 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 12.0-15.0 | 16.0-18.0 | – | 2.00-3.00 |
GB | 0.030 | 0.75 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 10.0-14.0 | 16.0-18.0 | 0.10 | 2.00-3.00 |
409 | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Ti % |
ASTM | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 0.50 | 10.5-11.7 | – | 6*C% – 0.75 |
DIN/EN | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
JIS | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.040 | 0.030 | – | 10.5-11.7 | – | 6*C% – 0.75 |
GB | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 0.60 | 10.5-11.7 | – | 6*C% – 0.75 |
310s | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Mo % |
ASTM | 0.08 | 1.50 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 19.0-22.0 | 24.0-26.0 | – | – |
DIN/EN | 0,10 | 1,50 | 2,00 | 0,045 | 0,015 | 19,0-22,0 | 24,0-26,0 | 0,10 | – |
JIS | 0.08 | 1.50 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 19.0-22.0 | 24.0-26.0 | – | – |
GB | 0.08 | 1.50 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 19.0-22.0 | 24.0-26.0 | – | – |
410S | C % | Si% | Mn % | P % | S % | Ni % | Cr % | N % | Mo % |
ASTM | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.040 | 0.030 | 0.60 | 11.5-13.5 | – | – |
DIN/EN | 0,08 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,040 | 0,015 | – | 12,0-14,0 | – | – |
JIS | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.040 | 0.030 | – | 11.5-13.5 | – | – |
GB | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.040 | 0.030 | 0.60 | 11.5-13.5 | – | – |
Main grade mechanical property in different standard
201 | Y.S./Mpa ≥ | T.S./Mpa ≥ | E.L./% ≥ | HB ≤ | HRB ≤ | HBW ≤ | HV ≤ |
ASTM | 260 | 515 | 40 | – | 95 | 217 | – |
JIS | 275 | 520 | 40 | 241 | 100 | – | 253 |
GB | 205 | 515 | 30 | - | 99 | – | - |
202 | Y.S./Mpa ≥ | T.S./Mpa ≥ | E.L./% ≥ | HB ≤ | HRB ≤ | HBW ≤ | HV ≤ |
ASTM | 260 | 620 | 40 | – | – | 241 | – |
JIS | 275 | 520 | 40 | – | 95 | 207 | 218 |
GB | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
304 | Y.S./Mpa ≥ | T.S./Mpa ≥ | E.L./% ≥ | HB ≤ | HRB ≤ | HBW ≤ | HV ≤ |
ASTM | 205 | 515 | 40 | – | 92 | 201 | – |
JIS | 205 | 520 | 40 | 187 | 90 | – | 200 |
GB | 205 | 515 | 40 | – | 92 | 201 | 210 |
316L | Y.S./Mpa ≥ | T.S./Mpa ≥ | E.L./% ≥ | HB ≤ | HRB ≤ | HBW ≤ | HV ≤ |
ASTM | 170 | 485 | 40 | – | 95 | 217 | – |
JIS | 175 | 480 | 40 | 187 | 90 | 200 | |
GB | 170 | 485 | 40 | – | 95 | 217 | 220 |
409 | Y.S./Mpa ≥ | T.S./Mpa ≥ | E.L./% ≥ | HB ≤ | HRB ≤ | HBW ≤ | HV ≤ |
ASTM | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
JIS | 175 | 360 | 22 | 162 | 80 | – | 175 |
GB | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
310s | Y.S./Mpa ≥ | T.S./Mpa ≥ | E.L./% ≥ | HB ≤ | HRB ≤ | HBW ≤ | HV ≤ |
ASTM | 205 | 515 | 40 | – | 95 | 217 | – |
JIS | 205 | 520 | 40 | 187 | 90 | – | 200 |
GB | 205 | 515 | 40 | – | 95 | 217 | 220 |
410S | Y.S./Mpa ≥ | T.S./Mpa ≥ | E.L./% ≥ | HB ≤ | HRB ≤ | HBW ≤ | HV ≤ |
ASTM | 205 | 415 | 22 | – | 89 | 183 | – |
JIS | 205 | 410 | 20 | – | 88 | 183 | 200 |
GB | 205 | 415 | 20 | – | 89 | 183 | 200 |
features of Stainless steel wire screw
Composition: 301 stainless steel is an austenitic stainless steel alloy containing chromium and nickel. It typically comprises 16-18% chromium and 6-8% nickel, along with small amounts of carbon and other elements. This composition imparts its excellent corrosion resistance and formability.
Work Hardening: One of the standout features of 301 stainless steel is its remarkable work hardening ability. This property means that as the material is deformed or shaped through mechanical processes like rolling or cold working, it becomes progressively stronger. This makes it ideal for applications that require higher levels of strength.
Structural Applications: Due to its capacity for work hardening, 301 stainless steel is commonly employed in structural applications where strength and durability are paramount. This includes the production of structural components in construction and engineering.
Mechanical Components: In addition to structural uses, 301 stainless steel is favored for manufacturing mechanical components. Its ability to become stronger with deformation makes it well-suited for parts and components that need to withstand stress and load-bearing requirements.
Corrosion Resistance: While the primary benefit of 301 stainless steel is its strength, it also retains good corrosion resistance. It can effectively resist corrosion when exposed to moisture and various environmental conditions.
In summary, 301 stainless steel is a versatile material known for its exceptional work hardening properties. Its suitability for applications requiring higher strength and its ability to withstand deformation make it a valuable choice for structural and mechanical components across a range of industries. Its corrosion resistance further enhances its desirability in various demanding environments.
- Composition: 302 stainless steel is derived from the popular 304 stainless steel alloy. The key difference lies in its higher carbon content. It typically contains about 0.15% carbon, compared to the lower carbon content of 304 stainless steel. This elevated carbon level contributes to its enhanced strength and durability.
Cold Rolling Process: To achieve its increased durability, 302 stainless steel undergoes a cold rolling process. Cold rolling is a mechanical process that involves reducing the thickness of the material while enhancing its mechanical properties. This process imparts the stainless steel with greater hardness and strength.
Strength and Corrosion Resistance: The combination of higher carbon content and cold rolling makes 302 stainless steel an ideal choice for applications that require both strength and corrosion resistance. It exhibits good tensile strength while retaining a degree of corrosion resistance, making it a versatile material.
Applications: Given its strength and corrosion resistance, 302 stainless steel is often utilized in applications where the material must withstand harsh conditions. These may include environments with elevated levels of moisture, humidity, or exposure to corrosive substances.
Versatility: The enhanced durability of 302 stainless steel makes it suitable for a wide range of applications. It is commonly employed in various industries, including manufacturing, construction, and the production of components and parts used in demanding conditions.
In summary, 302 stainless steel, derived from 304 stainless steel with increased carbon content and processed through cold rolling, offers a compelling combination of strength and corrosion resistance. It is an excellent choice for applications where durability and the ability to withstand harsh conditions are essential.
Stainless Steel Grades: These stainless steel cables are typically manufactured using grades like 304M, 304HC, and 316. These grades belong to the 300 series of austenitic stainless steel materials.
Austenitic Stainless Steel: The 300 series is known for its austenitic structure, which imparts remarkable corrosion resistance to the material. The austenitic structure consists of a face-centered cubic crystal lattice that is highly stable and resistant to corrosion, especially in various corrosive environments.
Corrosion Resistance: One of the primary attributes of these stainless steel grades is their exceptional corrosion resistance. This quality is of paramount importance in applications where exposure to moisture, chemicals, or other corrosive substances is common.
Outdoor and Marine Applications: Due to their superior resistance to corrosion, these stainless steel cables find extensive use in outdoor and marine environments. For example, they are employed in constructing marine rigging, sailboat rigging, and outdoor structures like cable railings and suspension bridges.
Chemical Processing: The resistance to corrosion and staining makes these stainless steel grades suitable for use in chemical processing plants. They are used in various components and equipment that come into contact with corrosive chemicals.
Industrial Uses: These stainless steel materials are also favored in a wide range of industrial applications. Their resistance to corrosion and the capacity to withstand harsh industrial environments make them versatile choices for applications such as conveyors, machinery, and manufacturing equipment.
Durability: Beyond corrosion resistance, stainless steel is known for its overall durability, which makes it a long-lasting material in various demanding scenarios. This durability ensures a prolonged service life, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
In summary, stainless steel cables, including those made from 304M, 304HC, and 316 grades, are valued for their exceptional corrosion resistance. They belong to the 300 series of austenitic stainless steels, known for their robust performance in marine, outdoor, chemical processing, and industrial applications. The inherent durability of stainless steel further solidifies its status as a preferred choice in situations where longevity and anti-corrosion properties are vital.
Composition: 316 stainless steel is often referred to as 18Cr-12Ni-2.5Mo, indicating its elemental composition. It consists of 18% chromium (Cr), 12% nickel (Ni), and 2.5% molybdenum (Mo), in addition to other elements.
Molybdenum Addition: What sets 316 stainless steel apart is the inclusion of molybdenum (Mo). This element plays a pivotal role in enhancing its properties.
Corrosion Resistance: Molybdenum significantly boosts the material’s corrosion resistance. It makes 316 stainless steel highly resistant to various corrosive environments, including those containing chlorides and other aggressive substances. This property is crucial in applications exposed to saltwater, acidic solutions, and chemical processing.
Atmospheric Corrosion Resistance: The presence of molybdenum further improves its resistance to atmospheric corrosion. This makes 316 stainless steel an excellent choice for outdoor applications and structures that are exposed to various weather conditions.
High-Temperature Strength: Another advantage of molybdenum is its contribution to high-temperature strength. 316 stainless steel can withstand elevated temperatures better than some other stainless steel grades. This makes it suitable for applications involving exposure to heat, such as industrial ovens and exhaust systems.
Non-Magnetic: Despite its enhanced properties, 316 stainless steel retains its non-magnetic nature. This is particularly important in industries where magnetic interference can be problematic, such as in electronics and medical equipment.
Work Hardening: 316 stainless steel exhibits excellent work hardening properties. This means that as the material is deformed or subjected to stress, it becomes stronger over time. This is advantageous in applications where the material needs to maintain its structural integrity under various loads.
Challenging Conditions: Due to its superior corrosion resistance, atmospheric corrosion resistance, and high-temperature strength, 316 stainless steel is the top choice for applications in challenging conditions. It is widely used in marine environments, chemical processing plants, and the pharmaceutical industry, among others.
In summary, 316 stainless steel, enhanced by the inclusion of molybdenum, offers exceptional corrosion resistance, atmospheric corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, and non-magnetic properties. Its ability to work harden makes it suitable for applications exposed to challenging conditions, making it a preferred material in various industries.
Hot Workability: 303Se stainless steel is known for its excellent hot workability, making it highly sought after for specific applications. Hot workability refers to the material’s ability to be easily forged, formed, or shaped at elevated temperatures without losing its desirable properties. This quality is particularly valuable in industries that involve hot forging processes.
Hot Forming Applications: 303Se stainless steel shines in applications that require hot forming. Hot forming processes involve heating the material to elevated temperatures to achieve the desired shape and properties. This stainless steel variant maintains its integrity and workability even under these high-temperature conditions, ensuring precise and effective hot forming results.
Hot Forging: Among the various applications, hot forging stands out as a prime use for 303Se stainless steel. In hot forging, the material is heated and then subjected to controlled pressure to shape it into the desired form. The excellent hot workability of 303Se stainless steel ensures that it can be efficiently forged at elevated temperatures, contributing to the quality and precision of the forged components.
Industries: 303Se stainless steel finds applications in industries where hot workability is crucial. This includes but is not limited to the manufacturing and forging sectors. The material is employed to create components that require hot forming or hot forging, as it retains its strength and malleability at elevated temperatures.
In summary, 303Se stainless steel is highly regarded for its exceptional hot workability, especially in hot forming and hot forging applications. Its ability to maintain its integrity and properties at elevated temperatures makes it a valuable choice for industries that rely on precision hot working processes.
Stainless steel wire screws, such as those made from 301, 302, and 316 stainless steel, offer remarkable corrosion resistance. They can withstand exposure to moisture, chemicals, and harsh environmental conditions. This property ensures their longevity in various applications.
Carbon Content: 304L stainless steel is a modified version of 304 stainless steel, and its key differentiator is the lower carbon content. The “L” in 304L stands for “Low,” indicating the reduced carbon content. The standard 304 stainless steel contains a higher amount of carbon compared to 304L.
Welding Applications: The primary purpose of using 304L stainless steel is in welding applications. The lower carbon content in 304L is particularly advantageous in welding. During the welding process, the heat can lead to the precipitation of carbides in the heat-affected zone near the weld. Carbides are compounds formed between carbon and other elements, and their presence can be problematic, especially in corrosive environments.
Intergranular Corrosion Prevention: The risk associated with higher carbon content in standard 304 stainless steel is the potential for intergranular corrosion in certain environments. Intergranular corrosion, also known as “welding erosion,” occurs along the grain boundaries of the material, where carbides can form. This type of corrosion can be detrimental, causing the material to lose its corrosion resistance.
Lower Precipitation of Carbides: The lower carbon content in 304L stainless steel minimizes the precipitation of carbides near the weld during the welding process. As a result, it significantly reduces the risk of intergranular corrosion. This makes 304L an ideal choice for applications where welding is required, especially in environments prone to corrosion.
Widespread Use: 304L stainless steel is widely used in various industries, including construction, automotive, and manufacturing, where welding is a common operation. By choosing 304L for welding applications, engineers and fabricators ensure that the material retains its excellent corrosion resistance even after welding.
In conclusion, 304L stainless steel is specifically tailored for welding applications. Its lower carbon content helps prevent the precipitation of carbides near the weld, reducing the risk of intergranular corrosion. This makes it a preferred choice in situations where welding and corrosion resistance are both essential.
Silicon Content: 302B stainless steel stands out due to its notably high silicon content. Silicon is a key alloying element in this stainless steel variant, contributing to its remarkable resistance to high-temperature oxidation. The typical silicon content in 302B stainless steel is significantly higher than in other stainless steel grades, enhancing its heat-resistant properties.
Heat Resistance: The elevated silicon content in 302B stainless steel makes it exceptionally heat-resistant. It can withstand high-temperature environments and is particularly suited for applications where exposure to extreme heat is a concern. This resilience to oxidation at elevated temperatures is a crucial feature for various industries.
Free Cutting: 302B stainless steel’s composition also makes it an excellent choice when free cutting properties are needed. This means it can be efficiently machined and processed, making it ideal for applications that require precision and smooth surfaces. This free cutting capability is valuable in various manufacturing processes.
High Surface Gloss: Another noteworthy aspect of 302B stainless steel is its ability to achieve high surface gloss. This makes it suitable for applications where an aesthetically pleasing finish is desired. It can be used to create components or parts that not only perform well under high-temperature conditions but also maintain a polished appearance.
Applications: 302B stainless steel is employed in situations where both its high-temperature resistance and free cutting properties are valuable. Industries that may benefit from this stainless steel variant include manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace, among others. It is used in the production of components and parts that operate in high-temperature environments and require precision machining.
In summary, 302B stainless steel’s exceptional resistance to high-temperature oxidation, coupled with its free cutting capabilities and ability to achieve high surface gloss, makes it a valuable choice for various applications. It is particularly well-suited for industries where heat resistance and precision machining are essential.
application of Stainless steel wire screws
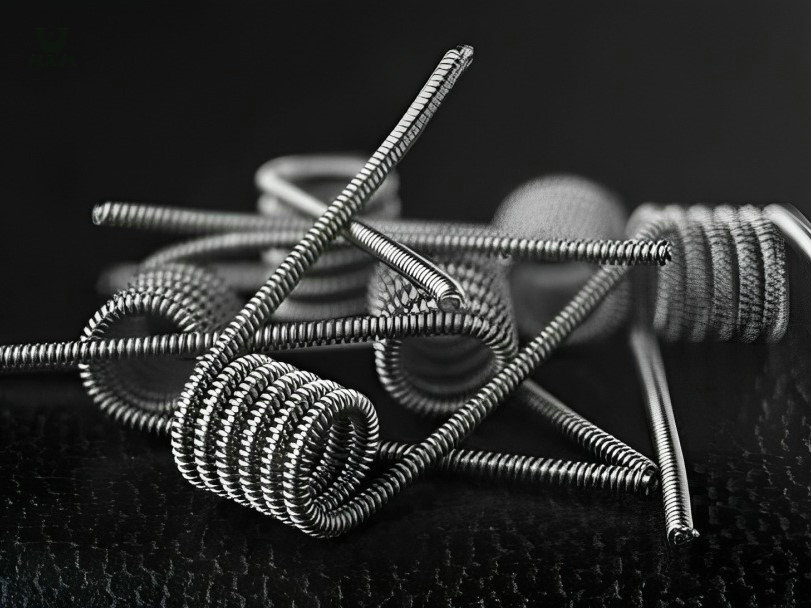
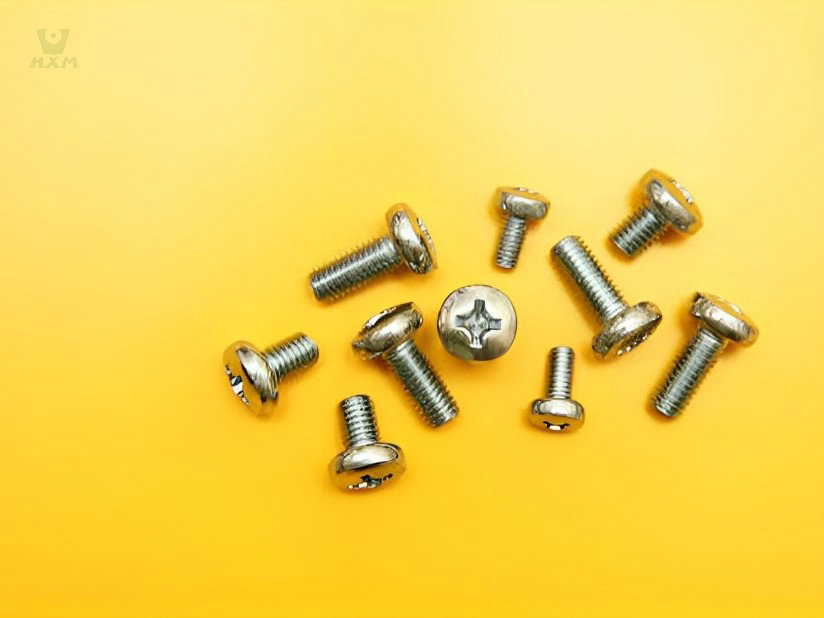
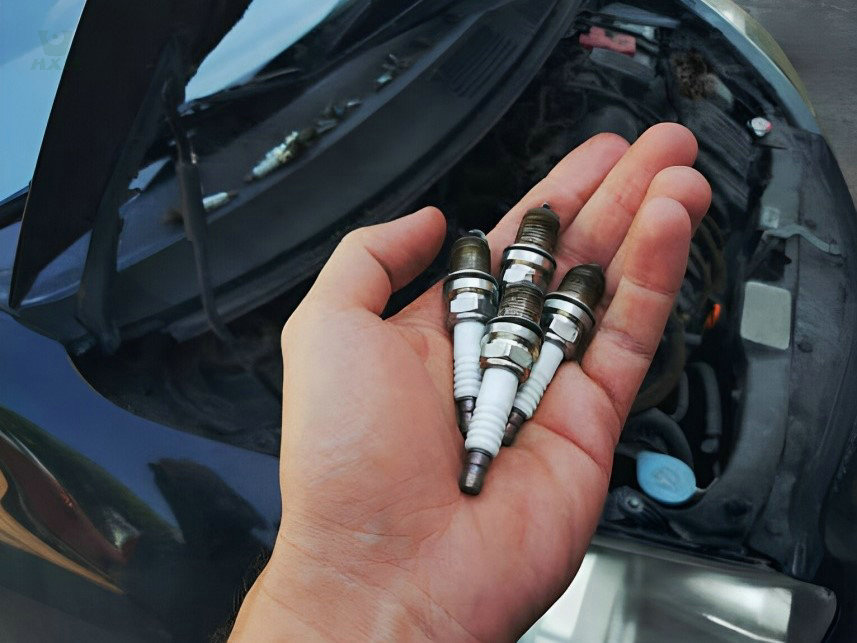


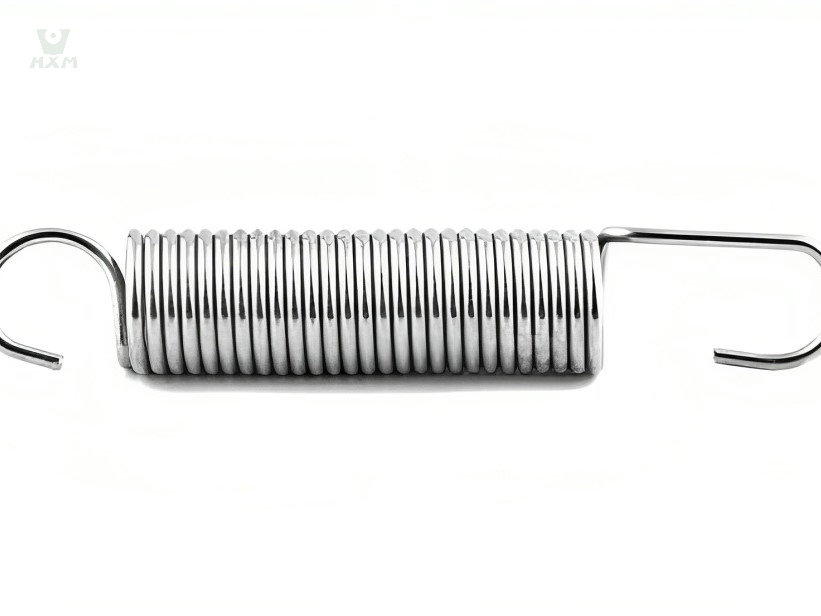


The main customers are Germany BECK, EASE FORTUNE, Japan and South Korea market and domestic high-end market, with a global market share of over 50%.
The objective of stainless steel screw cable: the hardness of stainless steel screw wire makes them be used for different functions. They are usually used as little screws in everyday life, but also as automobile compression and screws, which are frequently utilized in normal life. Kinds of stainless steel screw wires: in look, screw wires are usually split into matte spring cords and glistening screw wires. The hardness of matte screw wire is higher than that of shiny twist wire. It can be utilized as a hanger cord. For goods with low appearance requirements and higher elasticity requirements.
FAQ
A stainless steel wire screw is a type of fastener crafted from various grades of stainless steel and is designed to securely hold together a wide range of materials, including wood and various metals. These screws are manufactured by stainless steel wire manufacturers, utilizing their expertise in stainless steel materials to produce durable and corrosion-resistant fasteners suitable for numerous applications.
The strength of stainless steel wire screws varies depending on the specific alloy and grade used. Stainless steel is known for its strength and corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice for fasteners. However, it’s important to note that not all stainless steel grades are equally strong. Some stainless steel grades are weaker than hardened steel due to differences in their composition, especially carbon content. This makes it challenging to heat-treat certain alloys, affecting their overall strength. Stainless steel wire screws’ strength can be determined by the specific grade and alloy used, and stainless steel wire manufacturers play a crucial role in producing screws with the desired strength characteristics.
Stainless steel wire screws find versatile applications across various industries and projects. Their exceptional resistance to rust and corrosion makes them ideal for use in high humidity and contaminated environments. Some common areas where stainless steel wire screws are used include construction, marine applications, outdoor structures, chemical processing, food and pharmaceutical industries, and various industrial applications. Stainless steel wire manufacturers play a significant role in supplying these screws for a wide range of uses, ensuring their durability and anti-corrosion properties meet the demands of different environments and industries.
Stainless steel wire screws are highly resistant to rust when used outdoors. This resistance is attributed to their composition, which is primarily pure stainless steel. In comparison, some other fasteners might have a stainless steel coating over a core that is more susceptible to rust. This core advantage of pure stainless steel makes it a preferred choice for outdoor applications, ensuring durability and longevity even in harsh environmental conditions. Stainless steel wire manufacturers play a crucial role in providing these corrosion-resistant fasteners for outdoor use.
Determining whether a nail or screw is made of stainless steel involves several key characteristics. Stainless steel fasteners exhibit a distinct bright gray color with variations in shade when viewed from different angles. They often feature a fine brushed finish that offers a satin-like texture when touched. Another crucial trait is their non-magnetic nature, which sets them apart from ferromagnetic materials. These characteristics collectively indicate the stainless steel composition of the fastener, ensuring corrosion resistance and durability. Stainless steel wire manufacturers are instrumental in producing such stainless steel fasteners with these distinguishing features.
In the realm of miniature screws, we primarily offer two main materials: carbon steel and 18-8 stainless steel. These materials are chosen for their balance of strength and corrosion resistance. However, our capabilities extend beyond these options, and we can manufacture fasteners using various other materials to meet specific requirements. This includes materials like aluminum, 316 stainless steel, 316L stainless steel, and 410 stainless steel, allowing us to tailor the screws to different application needs. Stainless steel wire manufacturers play a pivotal role in this process, ensuring the production of high-quality miniature screws in various materials to cater to diverse industries and applications.
While stainless steel wire screws offer numerous advantages like high resistance to moisture and oxidation, and greater ductility, they are not inherently stronger than carbon steel in terms of tensile strength and hardness. Carbon steel generally possesses a higher tensile strength and is harder. However, the choice between stainless steel and carbon steel for specific applications often depends on the desired properties and environmental factors. Stainless steel wire manufacturers are pivotal in providing these options to meet diverse needs, ensuring the right balance between strength and other advantageous properties for various applications.
recent stainless steel wire products
Get In touch
Ready to Elevate Your Projects? Dive into our Stainless Steel Collection and Submit Your Specifications Today!
Phone/WhatsApp/WeChat:
+86 13052085117
Email: [email protected]
Address: RM557, NO.1388 Jiangyue Road, Shanghai China









